Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jul 15, 2023; 15(7): 1135-1148
Published online Jul 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i7.1135
Published online Jul 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i7.1135
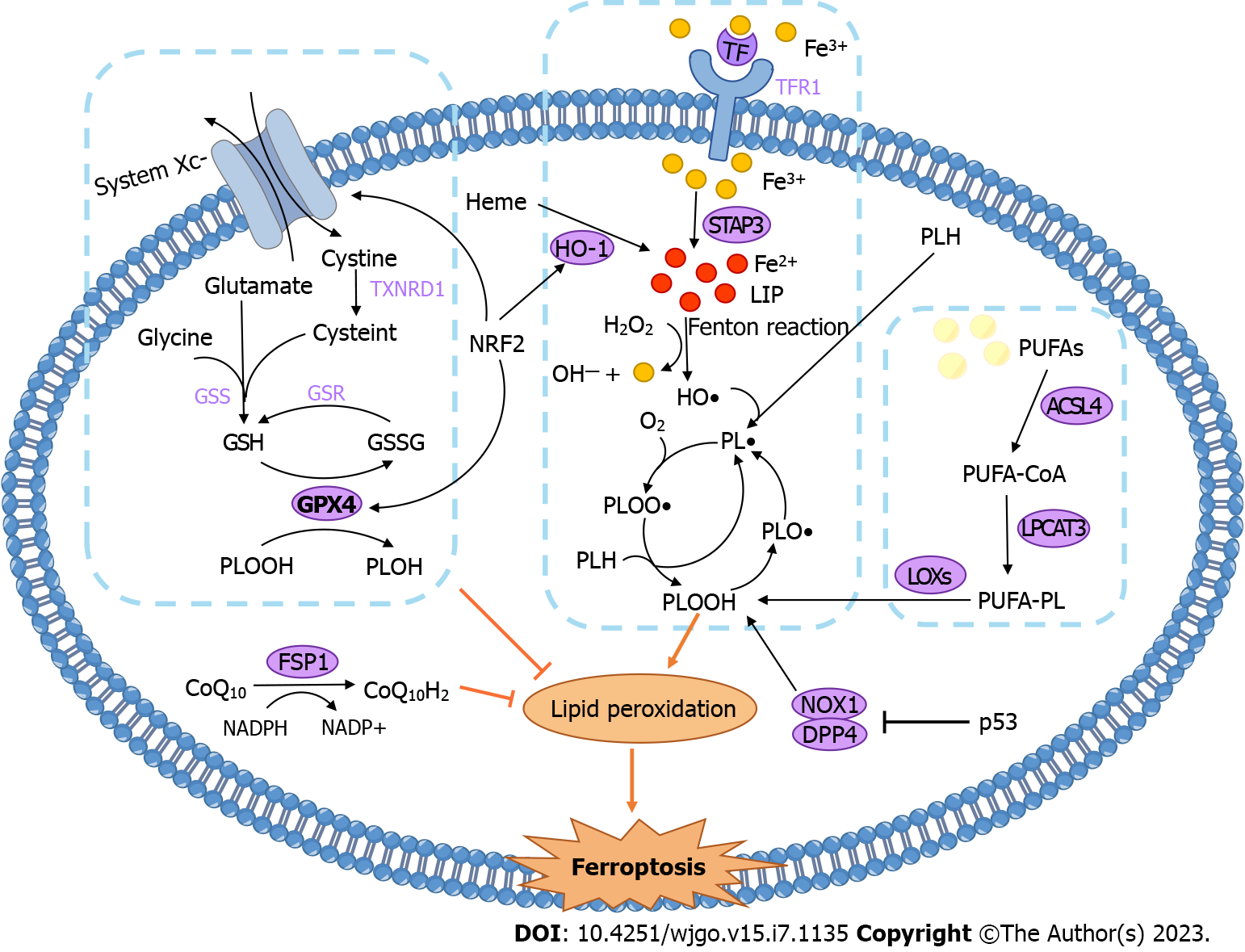
Figure 1 Mechanisms of ferroptosis (created by Figdraw).
TXNRD1: Thioredoxin reductase 1; GSS: Glutathione synthetase; GSH: Glutathione; GSSG: Oxidized glutathione; GSR: Glutathione-disulfide reductase; GPX4: Glutathione peroxidase 4; PLOOH: Phospholipid hydroperoxides; PLOH: Phosphatidyl alcohol; Fe3+: Ferric ion; Fe2+: Ferrous ion; TF: Transferrin; TfR1: Transferrin receptor 1; STEAP3: Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostate 3; LIP: labile iron pool; H2O2: Hydrogen peroxide; HO•: Hydroxyl radicals; PL•: Phospholipid radical; PLH: Phospholipid; PLO•: Phospholipid alkoxyl radical; PLOO•: Phospholipid peroxyl radical; PUFAs: Polyunsaturated fatty acids; PUFA-PL: Polyunsaturated-fatty-acid-containing phospholipid; ACSL4: Acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4; LPCAT3: Lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3; LOXs: Lipoxygenases; NRF2: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; HO-1: Haem oxygenase 1; FSP1: Ferroptosis suppressor protein 1; CoQ10: Ubiquinone; CoQ10H2: The reduced form of ubiquinone; p53: Tumor protein p53; DPP4: Dipeptidyl-peptidase-4; NOX1: A member of the NADPH oxidase protein family.
- Citation: Zeng XY, Qiu XZ, Wu JN, Liang SM, Huang JA, Liu SQ. Interaction mechanisms between autophagy and ferroptosis: Potential role in colorectal cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2023; 15(7): 1135-1148
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v15/i7/1135.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v15.i7.1135