Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. May 15, 2023; 15(5): 757-775
Published online May 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i5.757
Published online May 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i5.757
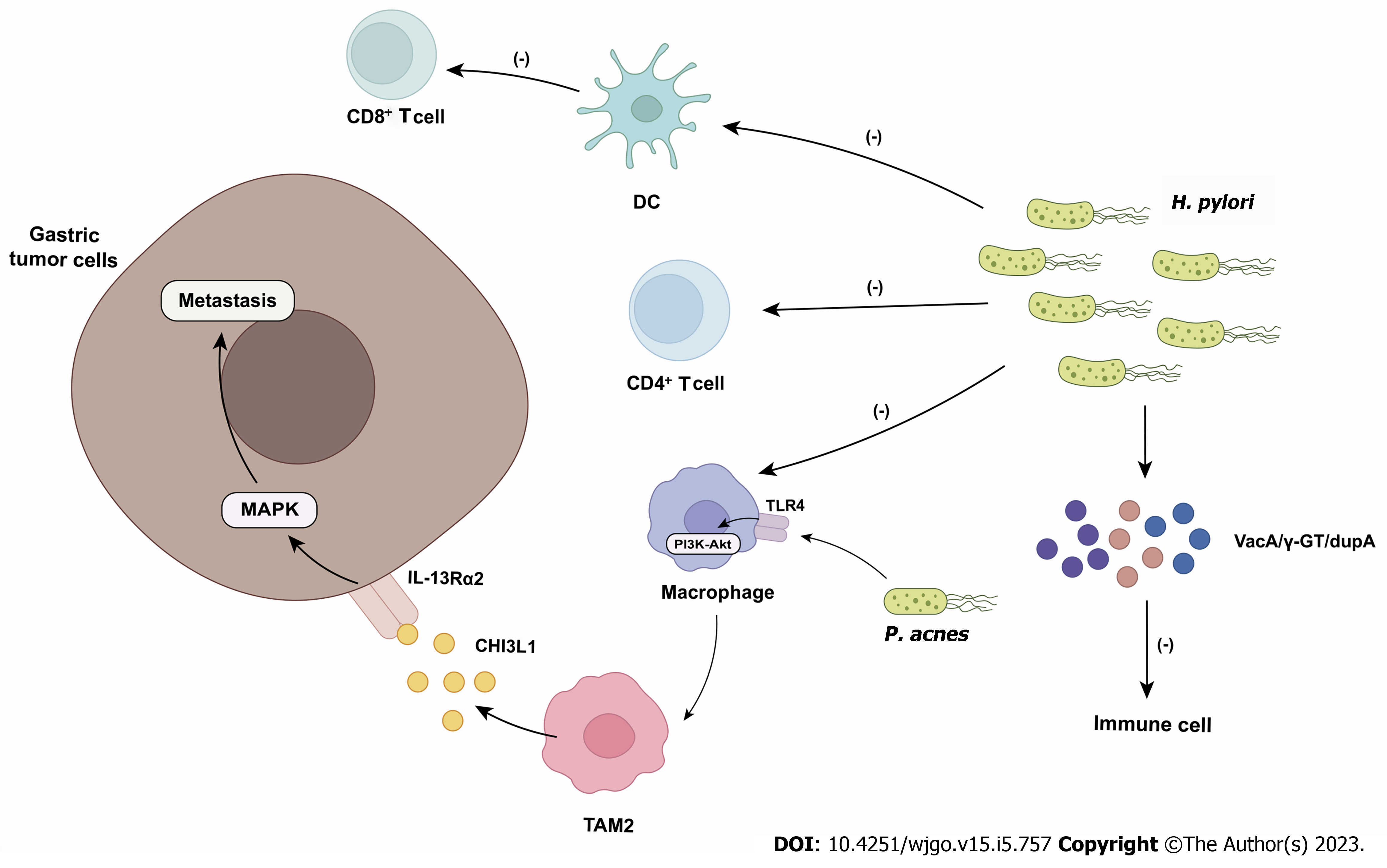
Figure 2 The role of microbiome in gastric cancer.
Helicobacter pylori inhibits the effector functions of CD4+ T cells, dendritic cells and macrophages and suppresses antitumor CD8+ T cell responses by altering the cross-presentation activity of dendritic cells. Helicobacter pylori also produce virulence factors (e.g., VacA, γ-GT, dupA) to impair immune cell activity. Propionibacterium acnes promote M2 polarization of macrophages via toll-like receptor 4/PI3K/Akt signaling. M2 macrophages secrete chitinase 3-like protein 1 that binds specifically to the interleukin-13 receptor α2 chai of tumor cells, triggering the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway and promoting gastric cancer metastasis. DC: Dendritic cell; TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; TAM: Tumor-associated macrophages; CHI3L1: Chitinase 3-like protein 1; IL-13Rα2: Interleukin-13 receptor α2 chain; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori; P. acnes: Propionibacterium acnes.
- Citation: Lin Q, Guan SW, Yu HB. Immuno-oncology-microbiome axis of gastrointestinal malignancy. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2023; 15(5): 757-775
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v15/i5/757.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v15.i5.757