Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Apr 15, 2023; 15(4): 596-616
Published online Apr 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i4.596
Published online Apr 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i4.596
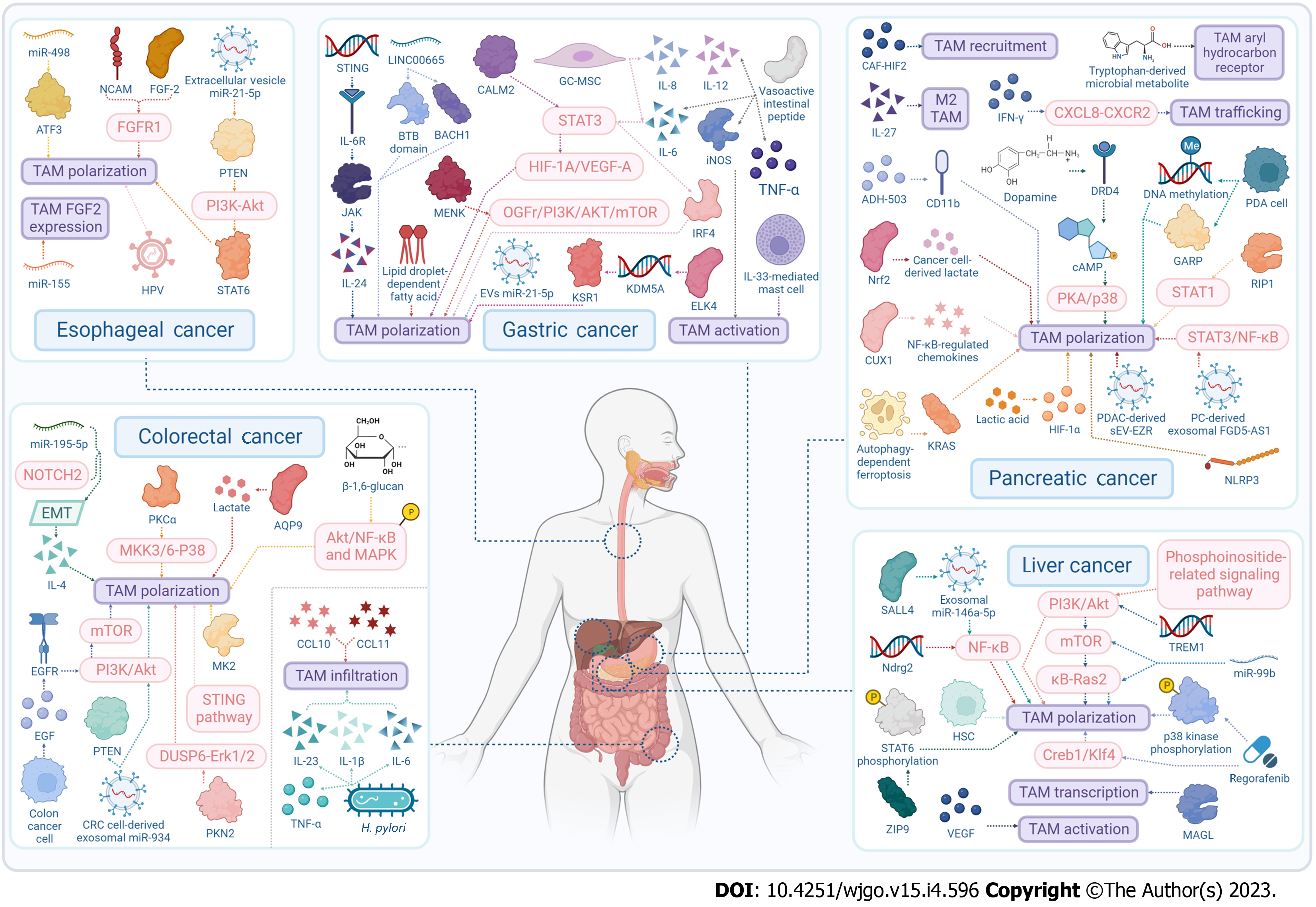
Figure 2 Tumor-associated macrophages act as potential therapeutic targets for tumors.
Multifarious strategies for modulation of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are unveiled for therapeutic applications, which are varying in different digestive system malignant tumors. Color differences indicate various approaches to regulate TAMs’ behaviors, the arrows represent secretory or regulatory behaviors, and braces represent combined action of the factors. Moreover, the pink icons stand for common signaling pathways, the green icons stand for biological processes, and the purple icons stand for different reactions of TAMs, including TAMs’ polarization, activation, recruitment, trafficking, infiltration, transcription, and so on. Tumor and immune cells secrete growth factors, cytokines, chemokines, metabolites and extracellular vesicles that promote TAM protumor polarization. Besides, RNA, virus and specific cells also exert influence on TAM plasticity and activation. Several key signaling pathways are involved in these regulation processes, including phosphoinositide 3-kinase-Akt-mammalian target of rapamycin, nuclear factor kB, stimulator of interferon genes, and so on. Thus, TAMs can act as a promising potential therapeutic target for digestive system malignant tumors. NCAM: Neural cell adhesion molecule; FGF-2: Fibroblast growth factor 2; ATF3: Activation transcription factor 3; TAM: Tumor-associated macrophages; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; HPV: Human papillomavirus; STAT3: Signal transducers and activator of transcription 3; STING: Stimulator of interferon genes; IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; NF-kB: Nuclear factor kB; MAGL: Monoacylglycerol lipase; TREM: Triggering receptors expressed on myeloid cells; EMT: Epithelial mesenchymal transition; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; HSC: Hematopoietic stem cell; GARP: Glycoprotein A repetitions predominant; IFN-γ: Interferon-γ; EVs: Extracellular vesicles; CCL: CC ligand; PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog.
- Citation: Shen Y, Chen JX, Li M, Xiang Z, Wu J, Wang YJ. Role of tumor-associated macrophages in common digestive system malignant tumors. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2023; 15(4): 596-616
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v15/i4/596.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v15.i4.596