Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Mar 15, 2023; 15(3): 504-522
Published online Mar 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i3.504
Published online Mar 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i3.504
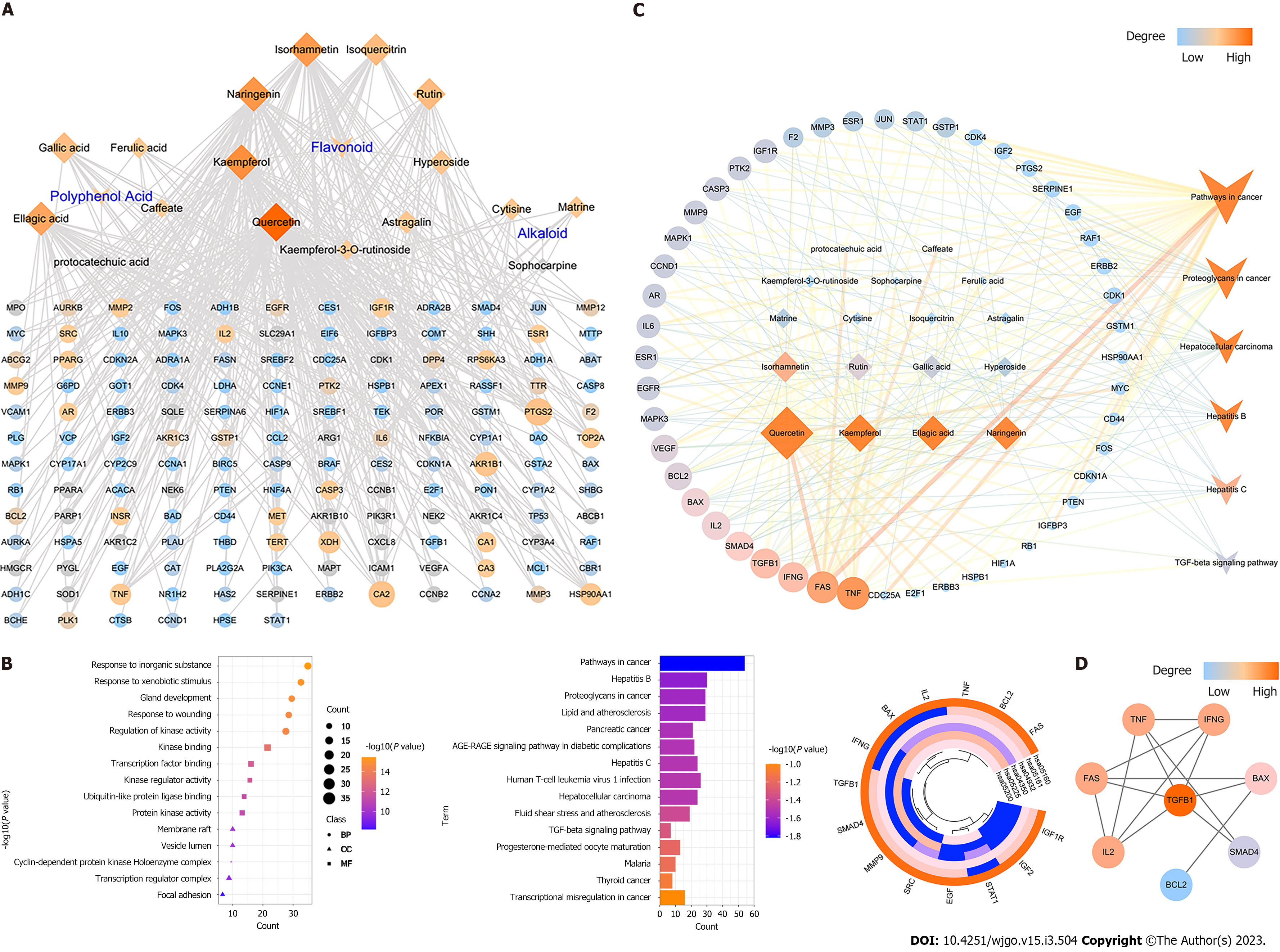
Figure 3 Network pharmacology construction and pathway enrichment analysis of Mu Ji Fang Granules.
A: Ingredients-anti-hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)-targets network of Mu Ji Fang Granules (MJF) (diamond represents ingredients and ellipse represents targets). The color of the nodes from blue to red indicate the degree from low the high; B: Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis and heatmap of the 14 most significantly different abundant genes related to the 6 KEGG pathways of HCC (BP: Represents Biological Process; CC: Represents Cellular Component; and MP: Represents Molecular Function); C: Ingredient-anti-HCC-pathway-target network of MJF (diamond represents ingredients, octagon represents targets and V represents pathway). The color of the nodes from red to yellow to green to blue indicates the degree from high to low; D: Hub targets of MJF most closely related to HCC. TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; TGF: Transforming growth factor; SMAD4: Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4; IL: Interleukin; FAS: TNF superfamily receptor 6.
- Citation: Zhang YB, Bao YR, Wang S, Li TJ, Tai H, Leng JP, Yang XX, Wang BC, Meng XS. Possible mechanisms associated with immune escape and apoptosis on anti-hepatocellular carcinoma effect of Mu Ji Fang granules. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2023; 15(3): 504-522
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v15/i3/504.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v15.i3.504