Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Nov 15, 2023; 15(11): 1974-1987
Published online Nov 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i11.1974
Published online Nov 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i11.1974
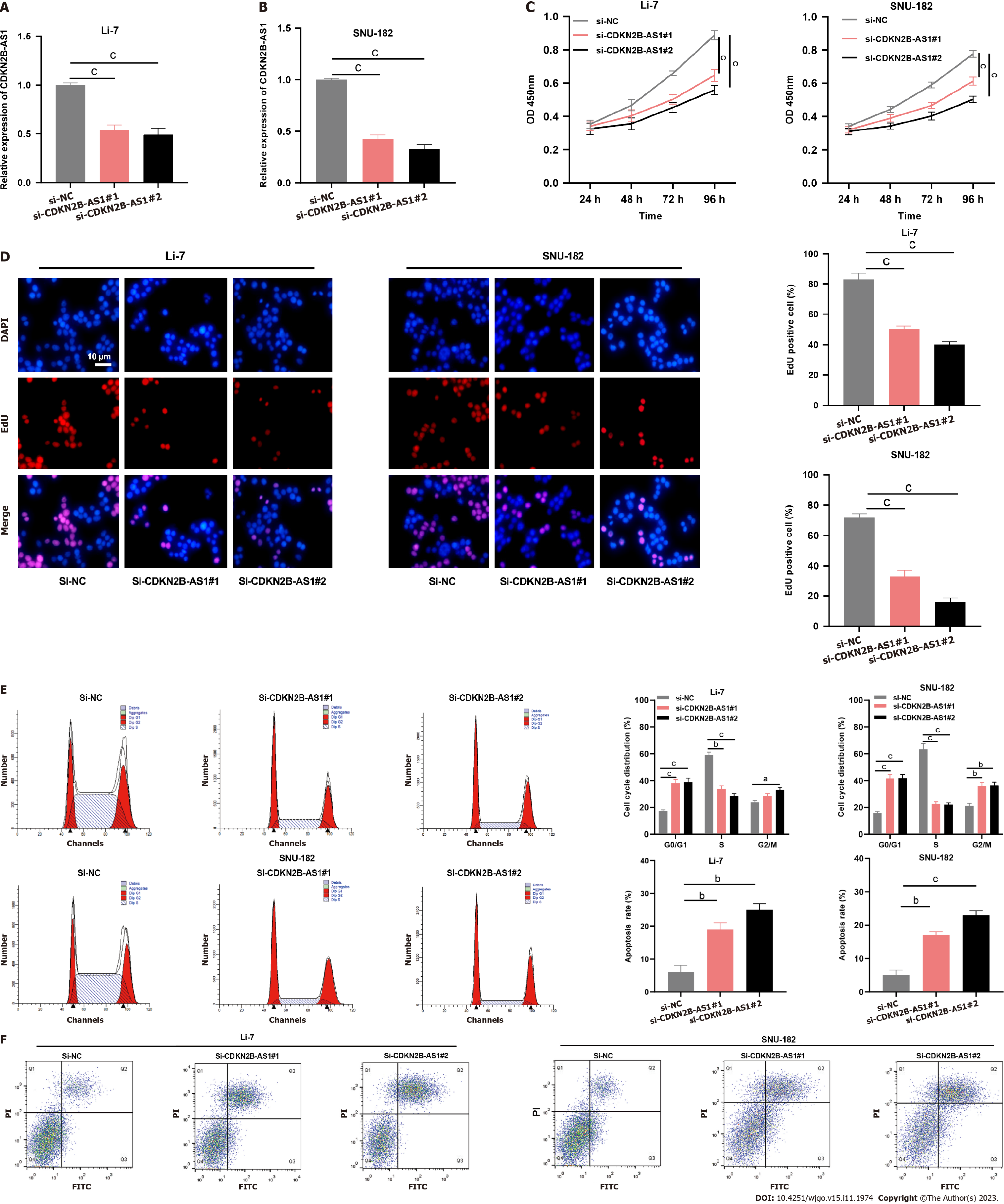
Figure 2 Depletion of CDKN2B-AS1 significantly inhibited the malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
A and B: Bar charts that demonstrate the validation results of transfection efficiency after silencing CDKN2B-AS1 in Li-7 (A) and SNU-182 (B) cell lines, which were evaluated by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; C: Line graphs showing proliferation changes in Li-7 (left) and SNU-182 (right) cells after CDKN2B-AS1 knockdown at different time points (24 h, 48 h, 72 h, 96 h); D: Images from EdU assay showing changes in DNA synthesis in Li-7 and SNU-182 cells after CDKN2B-AS1 knockdown. Bar charts summarize the quantitative results of EdU positive cells%; E and F: Flow cytometry results that reveal the effect of silencing of CDKN2B-AS1 on Li-7 and SNU-182 cell cycle (E) and apoptosis (F), E: (Left panel) cell cycle analysis results, the first and last peaks in red indicate G0-G1, G2-M stage, respectively, and the middle part indicates S stage; (right panel) bar charts summarizing cell cycle distribution%; F: (Left panel) dot plot diagrams showing apoptotic cell population changes in CDKN2B-AS1 silenced cells; (right panel) Bar charts summarizing apoptosis rate%. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 and cP < 0.001. PI: Propidium iodide.
- Citation: Tao ZG, Yuan YX, Wang GW. Long non-coding RNA CDKN2B-AS1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via E2F transcription factor 1/G protein subunit alpha Z axis. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2023; 15(11): 1974-1987
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v15/i11/1974.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v15.i11.1974