Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Sep 15, 2022; 14(9): 1637-1653
Published online Sep 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i9.1637
Published online Sep 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i9.1637
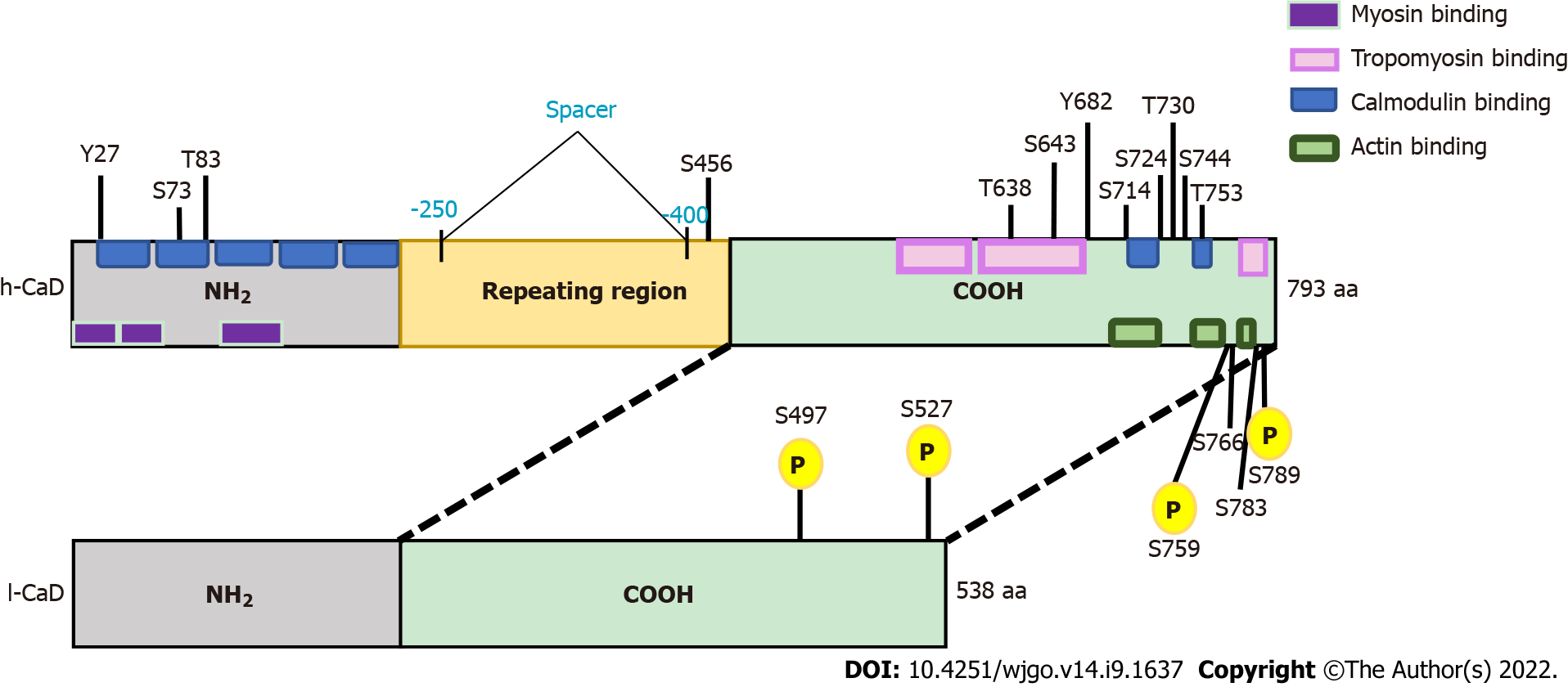
Figure 1 The domain structures of high-molecular-weight caldesmon and low-molecular-weight caldesmon.
Human caldesmon (CaD) has two major isoforms resulting from alternative splicing. The upper bar represents high-molecular-weight CaD (h-CaD) (793 aa), the full length protein, which contains an N-terminal domain (NH2), a C-terminal domain, and a middle part (repeating domain). The lower bar represents low-molecular-weight CaD (l-CaD) (538 aa), which is missing the middle repeating region. All functional domains are shared between h-CaD and l-CaD, except the missing central spacer in l-CaD that separates the N-terminal myosin binding domain from the C-terminal actin binding domain. Common functional regions for myosin and calmodulin are located within the NH2 terminal. The calmodulin binding site is also located in the C-terminal region. Tropomyosin and actin binding sites are found in the C-terminal region. Phosphorylation sites are shown and the shared phosphorylation sites for ERK and cdc2 are highlighted (yellow). h-CaD: High-molecular-weight caldesmon; l-CaD: Low-molecular weight caldesmon; NH2: N-terminal domain; COOH: C-terminal domain.
- Citation: Alnuaimi AR, Nair VA, Malhab LJB, Abu-Gharbieh E, Ranade AV, Pintus G, Hamad M, Busch H, Kirfel J, Hamoudi R, Abdel-Rahman WM. Emerging role of caldesmon in cancer: A potential biomarker for colorectal cancer and other cancers. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022; 14(9): 1637-1653
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v14/i9/1637.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v14.i9.1637