Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Aug 15, 2022; 14(8): 1499-1509
Published online Aug 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i8.1499
Published online Aug 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i8.1499
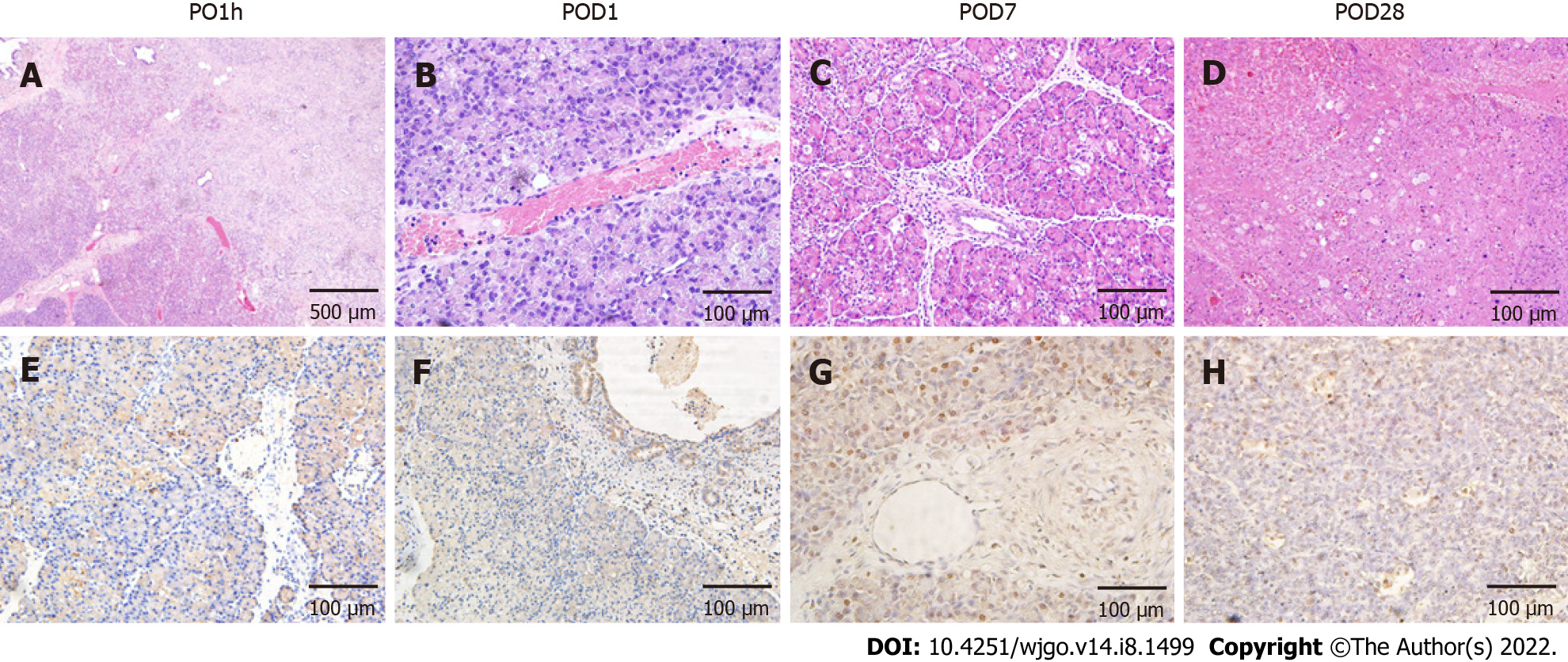
Figure 2 Effects of irreversible electroporation on pancreatic head tissue.
A: Hemotoxylin and eosin staining demonstrated extensive tissue damage in the irreversible electroporation (IRE) ablation zones with clear boundaries between ablation area and nonablation area; B-D: Tissue necrosis and immune cell infiltration were noted up to 4 wk post-IRE with gradual resolution and subsequent mild fibrosis; E-H: Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining revealed that the area centered on the probes in the ablation zone was strongly positive, and apoptotic expression was also seen in pancreatic ductal cells (F) and vascular endothelial cells (G). Scale bar in A = 500 μm. Scale bar in (B-H) = 100 μm. PO1h: Post-operative 1 h; POD: Post-operative day.
- Citation: Yan L, Liang B, Feng J, Zhang HY, Chang HS, Liu B, Chen YL. Safety and feasibility of irreversible electroporation for the pancreatic head in a porcine model. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022; 14(8): 1499-1509
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v14/i8/1499.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v14.i8.1499