Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jul 15, 2022; 14(7): 1356-1362
Published online Jul 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i7.1356
Published online Jul 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i7.1356
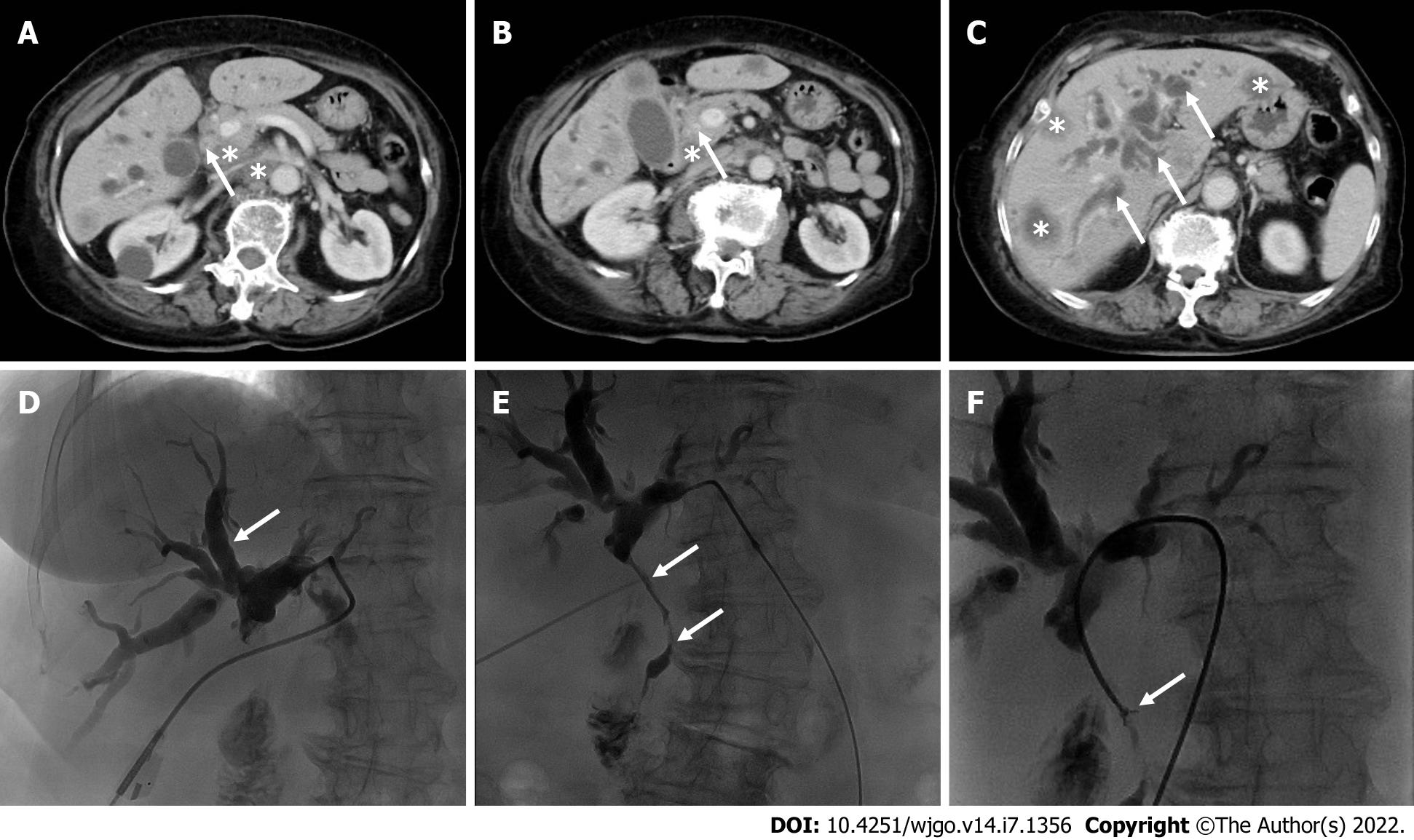
Figure 1 Contrast-enhanced computed tomography and percutaneous transhepatic cholangiopancreatic drainage images.
A and B: Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) of the abdomen shows that the common bile duct wall is thickened and strengthened (arrows) with enlarged lymph nodes (asterisks); C: CECT shows intrahepatic bile duct dilation (arrows) and multiple liver metastases (asterisks); D and E: Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiopancreatic drainage shows a vine-like expansion of the intrahepatic bile duct (D, arrows) and segmental stenosis of the extrahepatic bile duct (E, arrows); F: A biliary biopsy was performed under fluoroscopy (arrows).
- Citation: Xie CB, Wu Y, Li F, Zhao KF, Shi RS, Huang Q, Ao J, Ke D. Primary signet-ring cell carcinoma of the extrahepatic bile duct: A case report. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022; 14(7): 1356-1362
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v14/i7/1356.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v14.i7.1356