Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Apr 15, 2022; 14(4): 897-919
Published online Apr 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i4.897
Published online Apr 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i4.897
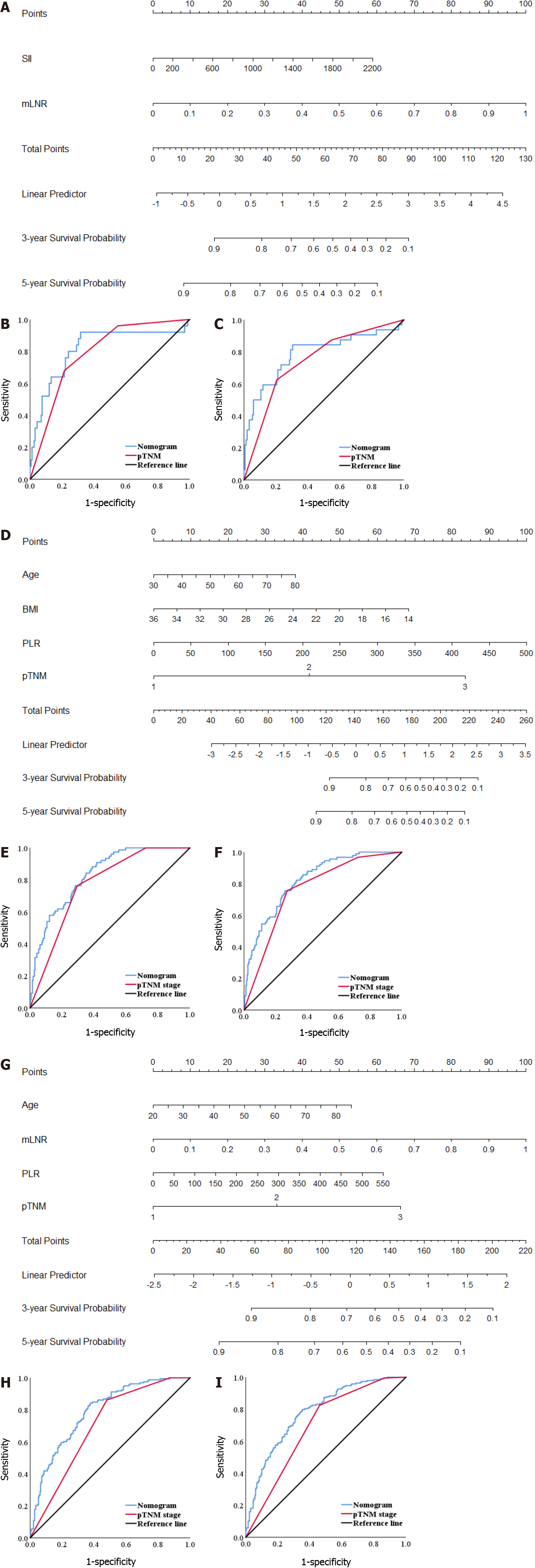
Figure 6 Nomogram models predicting the survival of patients with different tumor infiltrative pattern types.
A, D and G: Nomogram models predicting the 3-year and 5-year survival of patients with the expansive growth type (INFa), the intermediate type (INFb), and the infiltrative growth type (INFc) gastric cancer (GC); B and C: Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) of the nomogram model and postsurgical tumor node metastasis (pTNM) stage predicting the 3-year and 5-year survival of patients with INFa GC; E and F: ROC of the nomogram model and pTNM stage predicting the 3-year and 5-year survival of patients with INFb GC; H and I: ROC curve of the nomogram model and pTNM stage predicting the 3-year and 5-year survival of patients with INFc GC. INFa: The expansive growth type; INFb: The intermediate type; INFc: The infiltrative growth type; ROC: Receiver operating characteristic curve; mLNR: Metastatic lymph node ratio; BMI: Body mass index; PLR: Platelet-lymphocyte ratio; SII: Systemic immune-inflammation index.
- Citation: Wang YF, Yin X, Fang TY, Wang YM, Zhang L, Zhang XH, Zhang DX, Zhang Y, Wang XB, Wang H, Xue YW. Prognostic significance of serum inflammation indices for different tumor infiltrative pattern types of gastric cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022; 14(4): 897-919
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v14/i4/897.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v14.i4.897