Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Mar 15, 2022; 14(3): 703-715
Published online Mar 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i3.703
Published online Mar 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i3.703
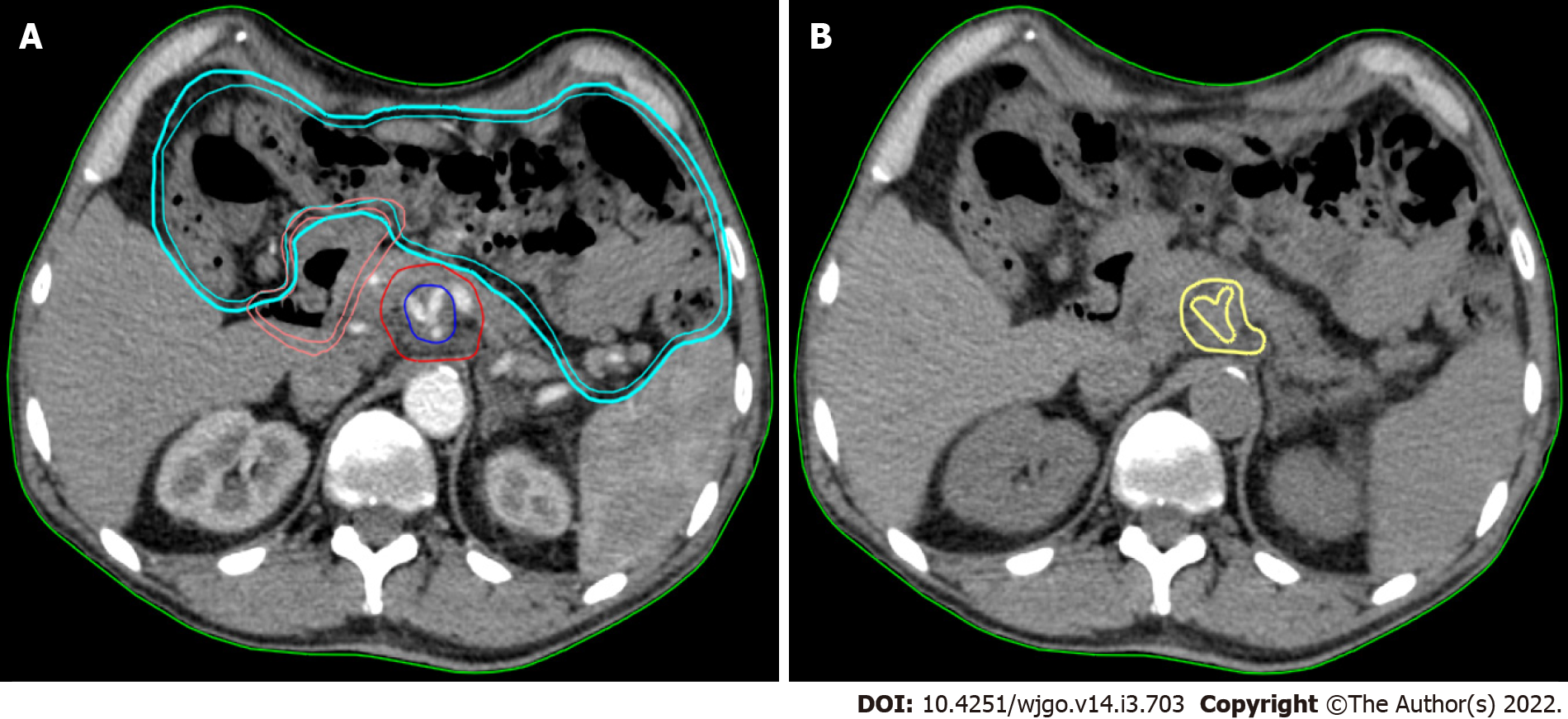
Figure 1 Texture analysis performed using contrast-free simulation computed tomography imaging.
A: Target volumes delineation in a stereotactic ablative radiation therapy case. The high-dose planning target volume (blue) encompasses the tumour-vessel interface (TVI, encasement of celiac axis) inside the tumour planning target volume (PTVt, red). The prescription dose is 30 Gy and 50 Gy in 5 fractions, with simultaneous integrated boost, to PTVt and TVI, respectively. The following organ at risk are shown: duodenum (pink) and bowel (cyan); B: The gross tumour volume (GTV) of the pancreatic lesion without vessels (yellow) is shown in the same axial computed tomography (CT)-simulation image without contrast. This is the final CT used for analysis.
- Citation: Rossi G, Altabella L, Simoni N, Benetti G, Rossi R, Venezia M, Paiella S, Malleo G, Salvia R, Guariglia S, Bassi C, Cavedon C, Mazzarotto R. Computed tomography-based radiomic to predict resectability in locally advanced pancreatic cancer treated with chemotherapy and radiotherapy. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022; 14(3): 703-715
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v14/i3/703.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v14.i3.703