Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Feb 15, 2022; 14(2): 450-477
Published online Feb 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i2.450
Published online Feb 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i2.450
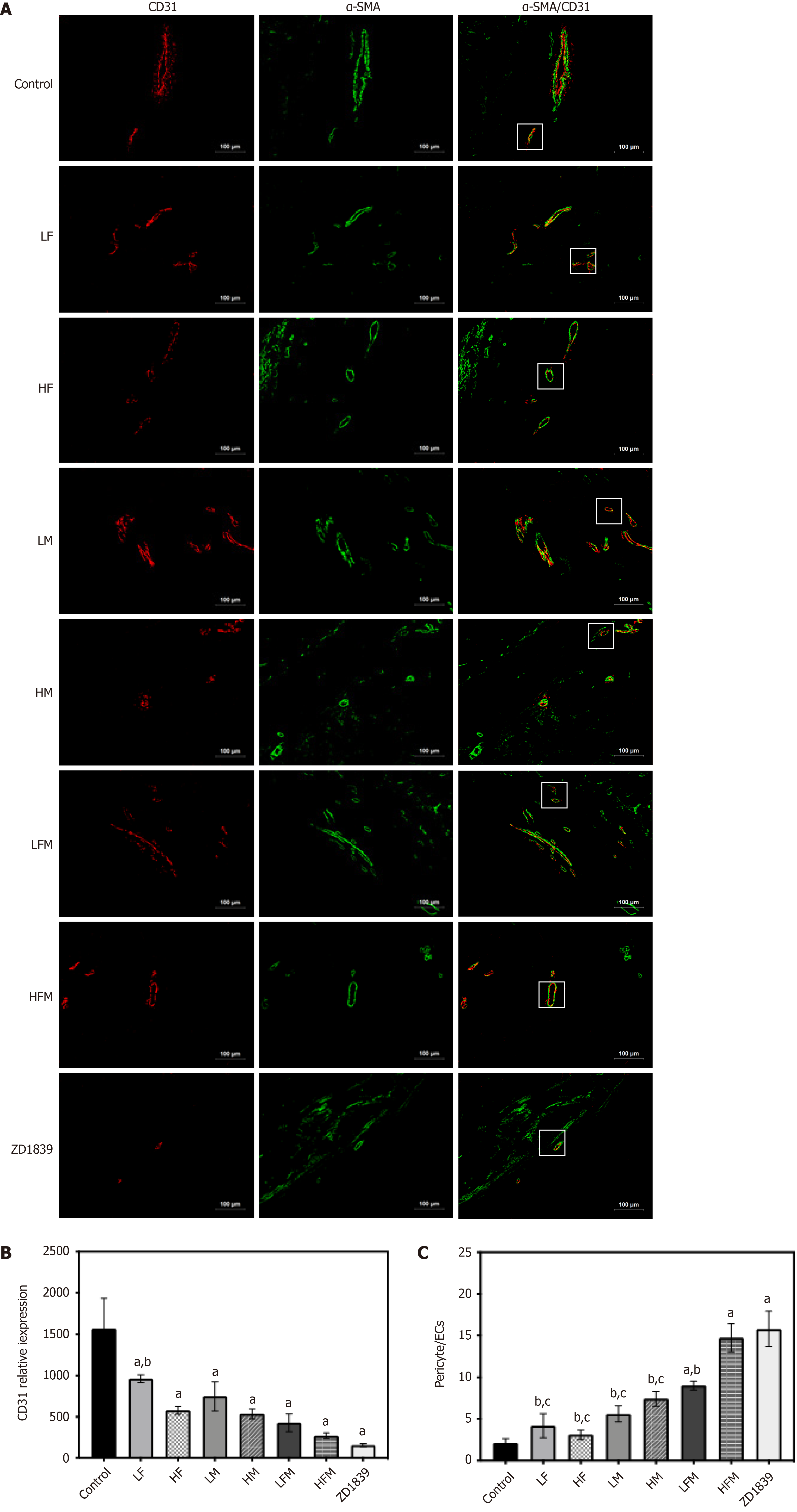
Figure 5 The effect of frankincense and/or myrrh on CD31 and α-SMA (200×).
A: Immunofluorescence staining of the tumor was indicated by CD31 antibody (red) and α-SMA antibody (green); B: The relative expression of CD31; C: The expression of α-SMA/CD31. Scale bars: 100 μm. LF: Low dose of frankincense extract; HF: High dose of frankincense extract; LM: Low dose of myrrh extract; HM: High dose of myrrh extract; LFM: Low dose of frankincense + myrrh extracts; HFM: High dose of frankincense + myrrh extracts. Data represents the mean ± SE. aP < 0.05 vs the model control; bP < 0.05 vs ZD1839; cP < 0.05 vs high dose of frankincense + myrrh extracts.
- Citation: Zheng P, Huang Z, Tong DC, Zhou Q, Tian S, Chen BW, Ning DM, Guo YM, Zhu WH, Long Y, Xiao W, Deng Z, Lei YC, Tian XF. Frankincense myrrh attenuates hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating tumor blood vessel development through multiple epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated signaling pathways. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022; 14(2): 450-477
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v14/i2/450.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v14.i2.450