Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Dec 15, 2022; 14(12): 2367-2379
Published online Dec 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i12.2367
Published online Dec 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i12.2367
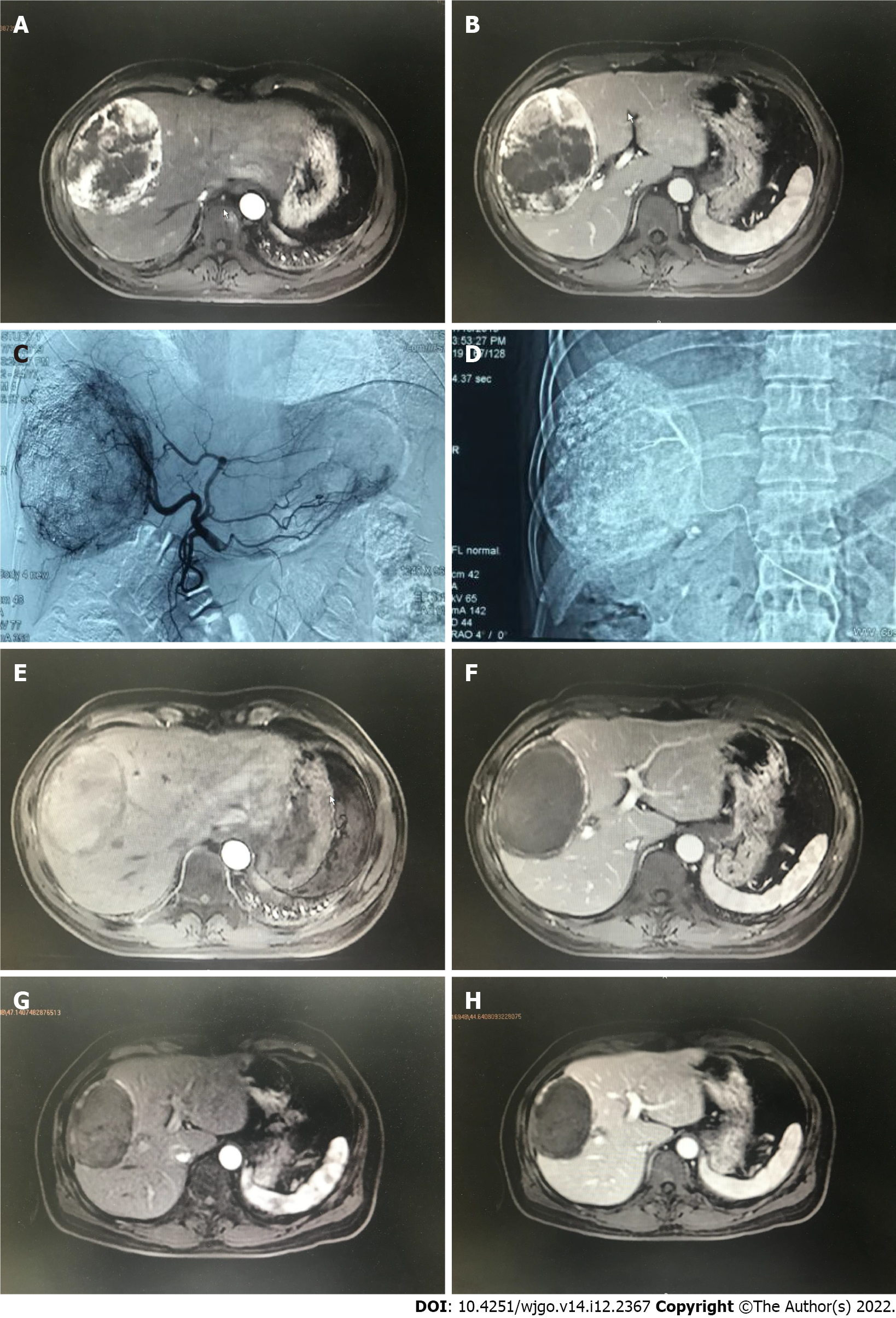
Figure 1 A 47 years old male diagnosed as primary liver cancer.
Preoperative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) T1WI enhanced axial position. A: In the arterial phase, there is a 105 mm × 85 mm × 119 mm uneven abnormal enhancement of the right lobe of the liver; B: The portal vein can be cleared. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization treatment with drug-loaded microspheres was performed in July 2019; C: Digital subtracted angiography under common hepatic arteriography during interventional surgery shows tumors with rich blood supply in the right lobe of the liver; D: Microcatheter superselection of the right hepatic artery for chemoembolization; E: A 103 mm × 69 mm × 109 mm mass in the right lobe of the liver can be seen in the arterial phase and no obvious enhancement is seen; F: There is no enhancement in the mass in the portal vein; G: MRI T1WI enhancement axis is re-examined 3 mo after the operation. The mass in the right lobe of the liver in the arterial phase is compared to the previous significantly reduced (86 mm × 57 mm × 88 mm); H: There was no enhancement of the portal venous mass.
- Citation: Ye T, Shao SH, Ji K, Yao SL. Evaluation of short-term effects of drug-loaded microspheres and traditional transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in the treatment of advanced liver cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022; 14(12): 2367-2379
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v14/i12/2367.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v14.i12.2367