Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Dec 15, 2022; 14(12): 2340-2352
Published online Dec 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i12.2340
Published online Dec 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i12.2340
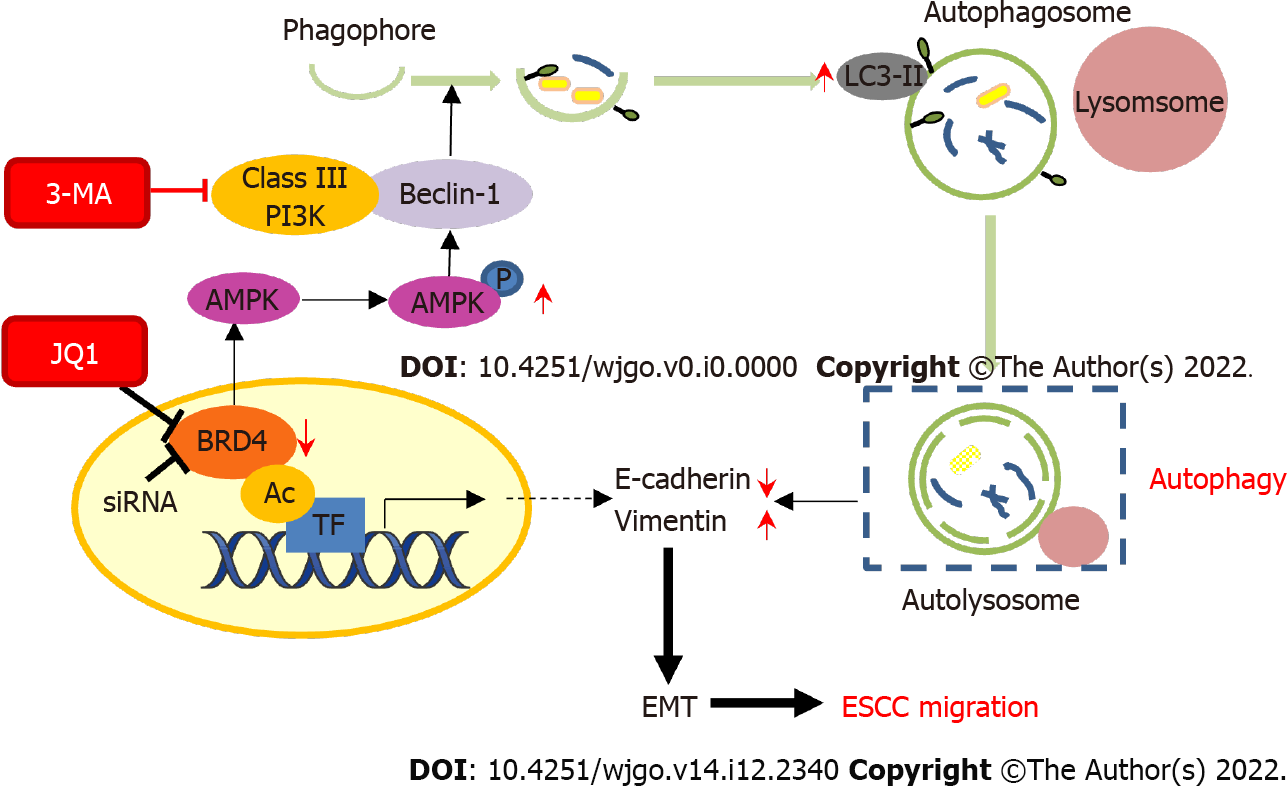
Figure 5 Schematic model of the effect of JQ1 or inhibition of bromodomain-containing protein 4 on cell migration in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells.
JQ1 treatment or siRNA inhibition of bromodomain-containing protein 4 can lead to increased phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase, resulting in upregulation of LC3-II protein level in order to activate autophagy. In addition, the activation of autophagy promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition process of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells, thus promoting the JQ1-induced migration of esophageal cancer cells. Finally, this pro-migration effect can be inhibited by the autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine. AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; TF: Transcription factor; BRD4: Bromodomain-containing protein 4; EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; ESCC: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; AC: Acetylation.
- Citation: Yang WQ, Liang R, Gao MQ, Liu YZ, Qi B, Zhao BS. Inhibition of bromodomain-containing protein 4 enhances the migration of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells by inducing cell autophagy. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022; 14(12): 2340-2352
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v14/i12/2340.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v14.i12.2340