Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Oct 15, 2022; 14(10): 1981-2003
Published online Oct 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i10.1981
Published online Oct 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i10.1981
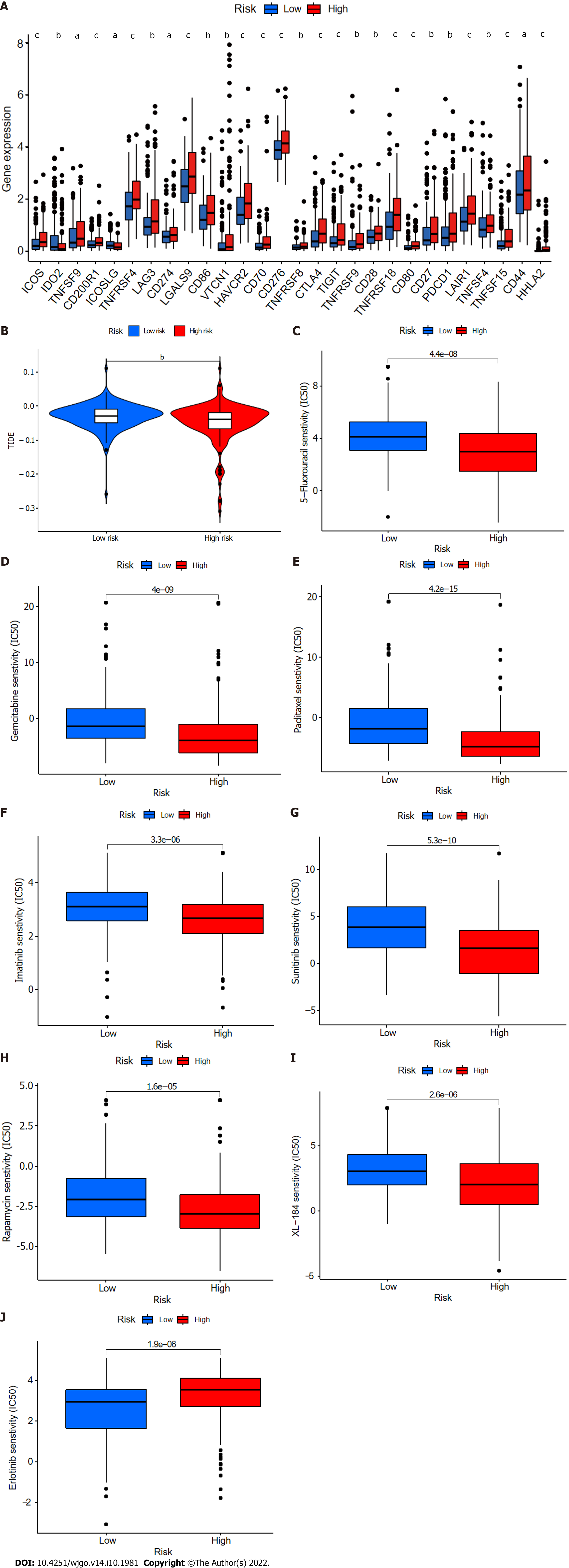
Figure 11 Comparison of immune checkpoints, tumor immune dysfunction, and exclusion module scores, and chemotherapy and targeted therapy drug efficacy in high- and low-risk groups.
A: Expression of 28 immune checkpoint genes differed between the high- and low-risk groups. Red and blue boxes represent high- and low-risk patients, respectively; B: Online software tumor immune dysfunction (TIDE) predictions of outcomes in HCC subgroups treated with either anti-PD1 or anti-CTLA4 therapy. A higher TIDE score suggests a greater likelihood of tumor immune escape and a poorer response to immunotherapy; C-J: IC50 values for (C) 5-fluorouracil, (D) gemcitabine, (E) paclitaxel, (F) imatinib, (G) sunitinib, (H) rapamycin, (I) XL-184 (cabozantinib), and (J) erlotinib in high- and low-risk groups. IC50, half-maximal inhibitory concentration. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. NS: Not significant.
- Citation: Huang EM, Ma N, Ma T, Zhou JY, Yang WS, Liu CX, Hou ZH, Chen S, Zong Z, Zeng B, Li YR, Zhou TC. Cuproptosis-related long non-coding RNAs model that effectively predicts prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022; 14(10): 1981-2003
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v14/i10/1981.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v14.i10.1981