Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Oct 15, 2022; 14(10): 1981-2003
Published online Oct 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i10.1981
Published online Oct 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i10.1981
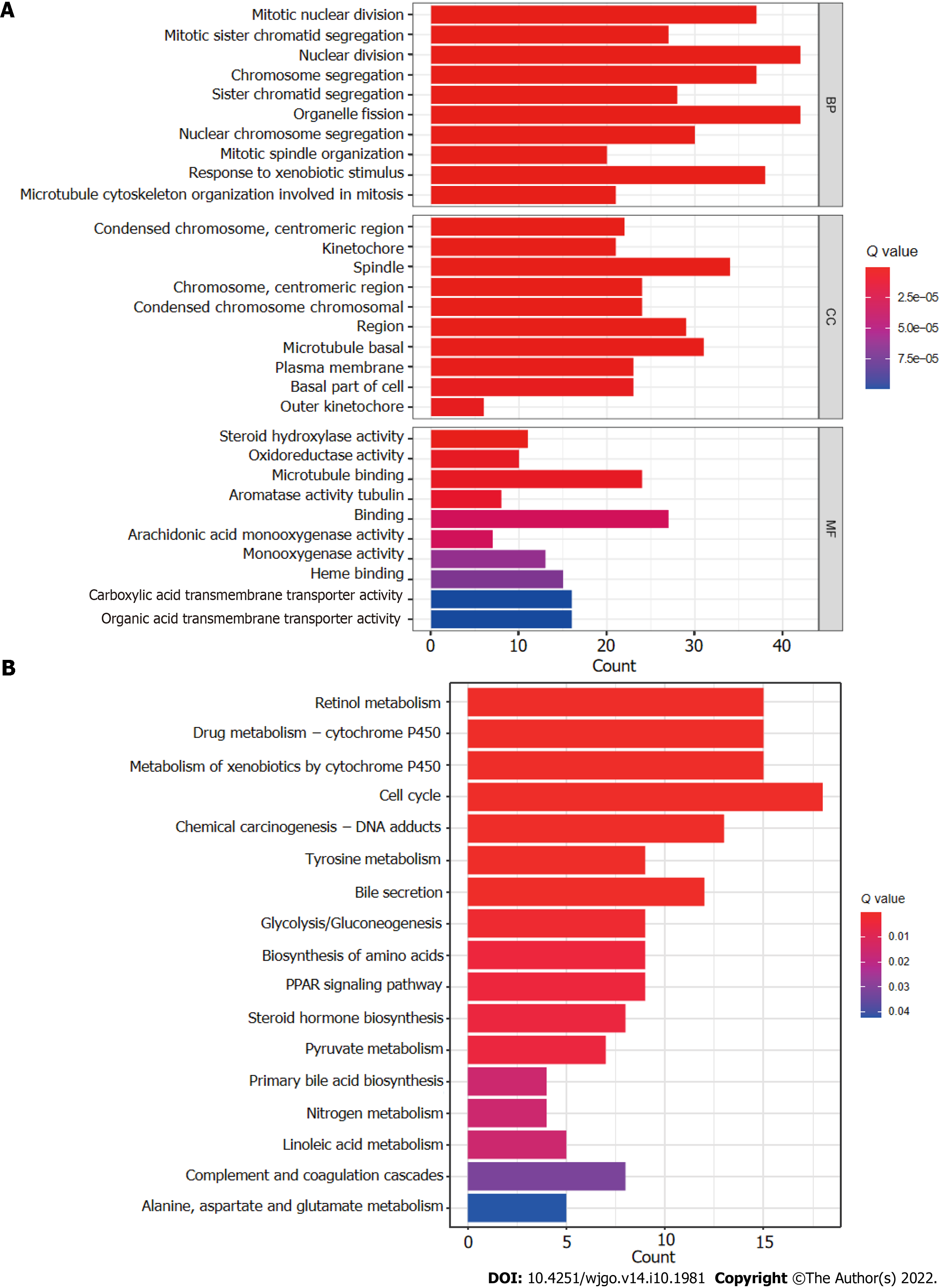
Figure 8 Gene set functional annotation of differentially expressed genes and long-chain non-coding RNAs in high- and low-risk hepatocellular carcinoma groups.
A: In gene ontology analysis, differentially expressed genes and long-chain non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) were found to be most enriched in biological process terms mitotic nuclear division, mitotic sister chromatid segregation, nuclear division, chromosome segregation, and sister chromatid segregation; in cellular component terms condensed chromosomes, kinetochores, spindles, chromosomes, and condensed chromosomes; and in molecular function terms steroid hydroxylase activity, oxidoreductase activity, microtubule binding, aromatase activity, and tubulin binding; B: Differentially expressed genes and lncRNAs were found to be most enriched in the following five Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways: retinol metabolism, cytochrome P450 drug metabolism, cytochrome P450 xenobiotic metabolism, cell cycle, and chemical carcinogenesis-DNA adducts. BP: Biological process; CC: Cellular component; MF: Molecular function.
- Citation: Huang EM, Ma N, Ma T, Zhou JY, Yang WS, Liu CX, Hou ZH, Chen S, Zong Z, Zeng B, Li YR, Zhou TC. Cuproptosis-related long non-coding RNAs model that effectively predicts prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022; 14(10): 1981-2003
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v14/i10/1981.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v14.i10.1981