Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Oct 15, 2022; 14(10): 1981-2003
Published online Oct 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i10.1981
Published online Oct 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i10.1981
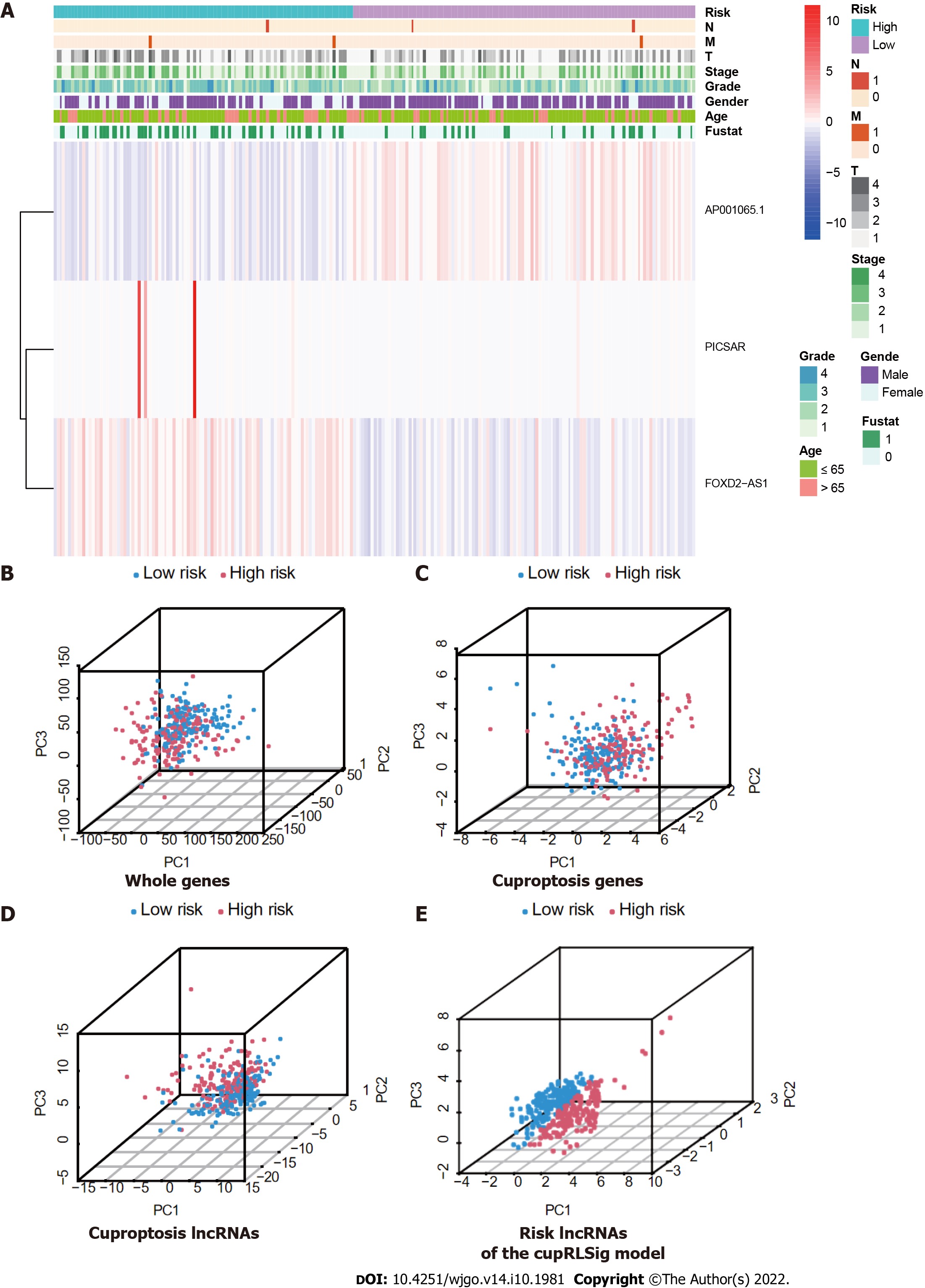
Figure 5 Visualization of expression levels of the three component long-chain non-coding RNAs of the cuproptosis-related long-chain non-coding RNA signature (CupRLSig) model based on clinicopathological variable stratification and principal component analysis of different gene sets performed for classification of patient risk.
A: Heatmaps of expression of the three long-chain non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and clinical characteristics for different risk groups; B-E: PCA of low- and high-risk groups based on (B) whole-genome genes, (C) cuproptosis-related genes, (D) cuproptosis-related lncRNAs, and (E) cuproptosis-related lncRNA signature (CupRLSig) model risk lncRNAs. Patients with high risk scores are denoted by red, while those with low risk scores are denoted by blue. N: Lymph node metastasis; M: Mistant metastasis; T: Tumor.
- Citation: Huang EM, Ma N, Ma T, Zhou JY, Yang WS, Liu CX, Hou ZH, Chen S, Zong Z, Zeng B, Li YR, Zhou TC. Cuproptosis-related long non-coding RNAs model that effectively predicts prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022; 14(10): 1981-2003
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v14/i10/1981.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v14.i10.1981