Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Oct 15, 2022; 14(10): 1933-1948
Published online Oct 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i10.1933
Published online Oct 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i10.1933
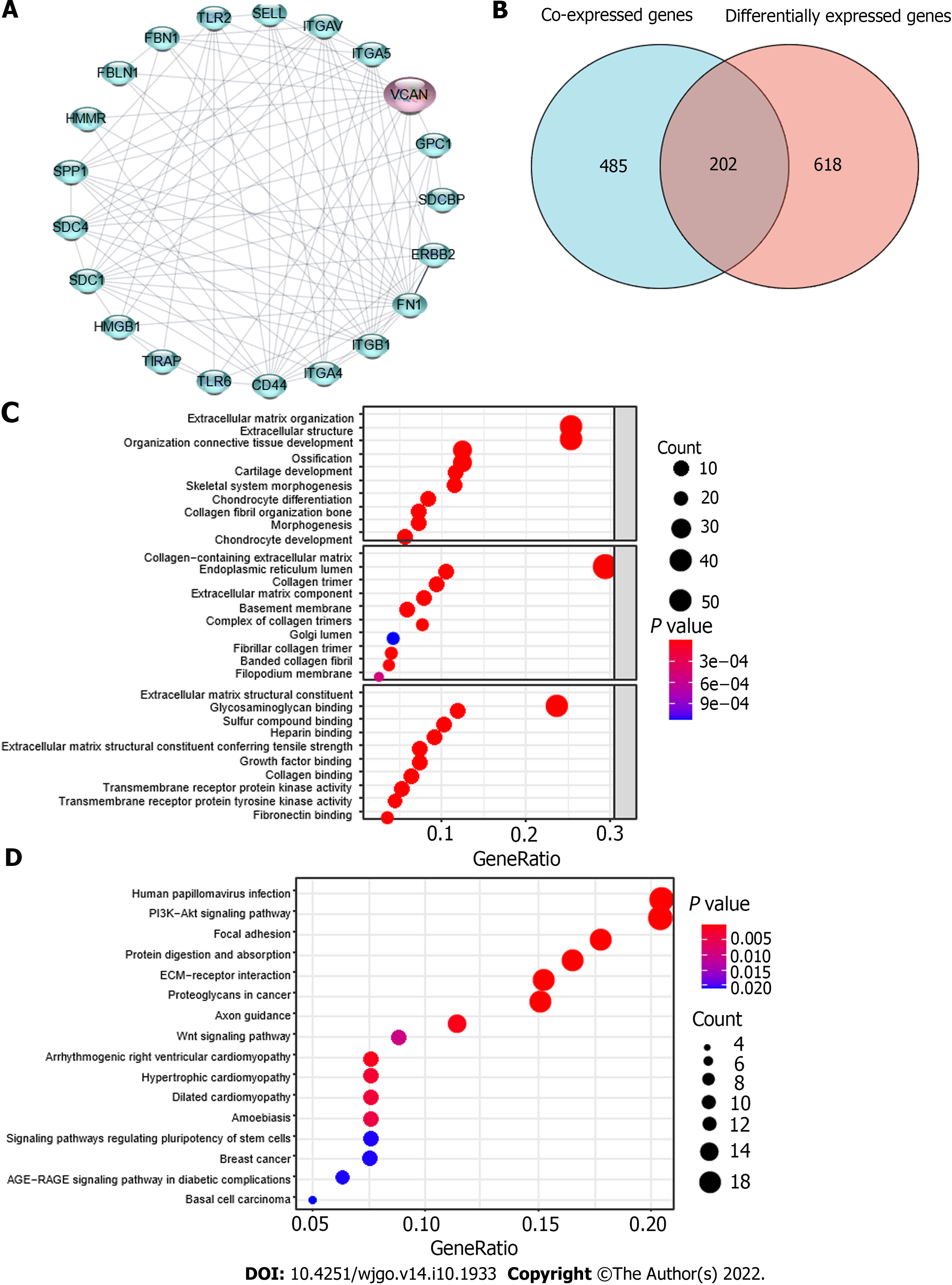
Figure 6 Possible mechanism of action of VCAN in hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Protein-protein interaction analysis of VCAN on STRING; B: Venn diagram for VCAN co-expressed genes and differentially expressed genes in high VCAN group and low VCAN group; C: Gene Ontology analysis of the 202 intersection genes; D: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analysis of the 202 intersection genes. HMMR: Hyaluronan mediated motility receptor; FBLN1: Fibulin-1; FBN1: Fibrillin-1; TLR2: Toll-like receptor 2; SELL: L-selectin; ITGAV: Integrin alpha-V; ITGA5: Integrin alpha-5; GPC1: Glypican-1; SDCBP: Syntenin-1; ERBB2: Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2; FN1: Fibronectin 1; ITGB1: Integrin beta-1; ITGA4: Integrin alpha-4; CD44: CD44 antigen; TIRAP: Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain-containing adapter protein; HMGB1: High mobility group protein B1; SDC: Syndecan; SPP1: Secreted phosphoprotein 1.
- Citation: Wang MQ, Li YP, Xu M, Tian Y, Wu Y, Zhang X, Shi JJ, Dang SS, Jia XL. VCAN, expressed highly in hepatitis B virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma, is a potential biomarker for immune checkpoint inhibitors. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022; 14(10): 1933-1948
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v14/i10/1933.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v14.i10.1933