Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jan 15, 2022; 14(1): 75-89
Published online Jan 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i1.75
Published online Jan 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i1.75
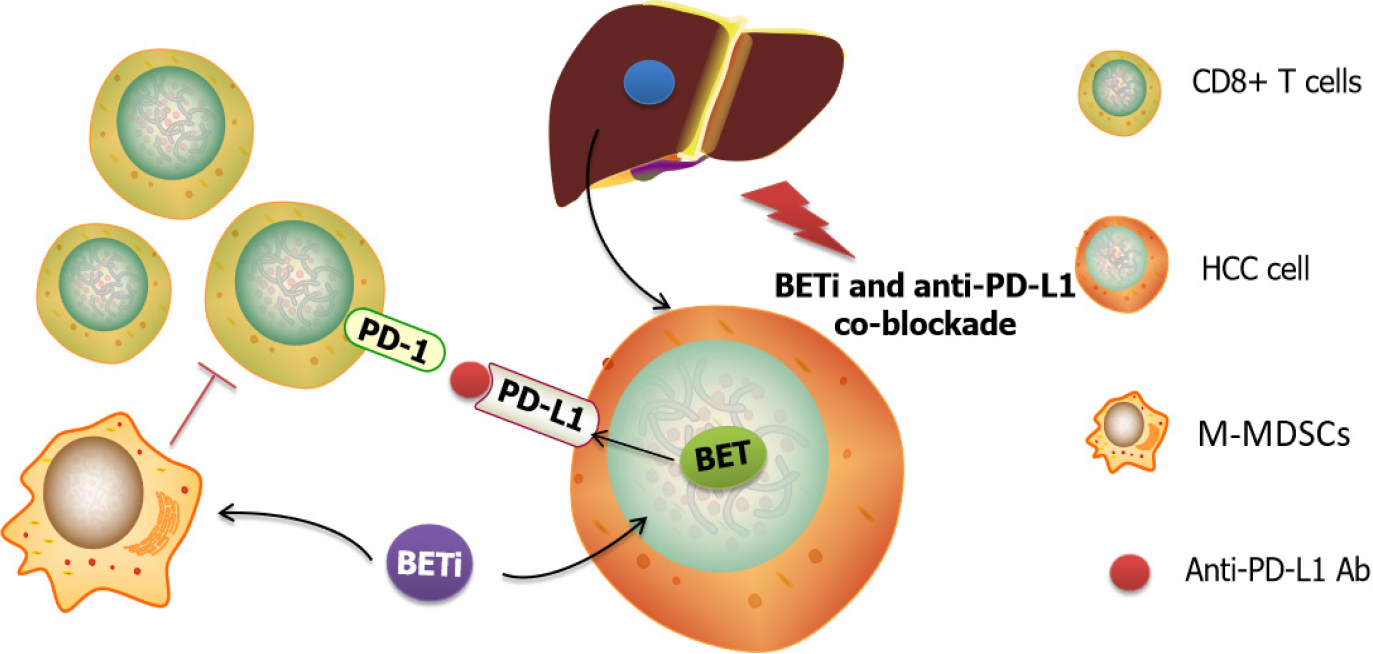
Figure 4 Schematic of Bromodomain and extra-terminal inhibitors combined with anti-programmed death-1-ligand-1 Ab therapeutic effects.
Bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) inhibitors treatment impacts programmed death-1-ligand-1 (PD-L1) expression, resulting in sensitizing the liver response to anti-PD-L1 blockade. Also, the co-inhibition can inhibit liver-infiltrating monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells and enhance tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells, which contributes to the elimination of drug resistance. BET: Bromodomain and extra-terminal; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; M-MDSCs: Monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells; PD-L1: Programmed death-1-ligand-1.
- Citation: Sun HY, Du ST, Li YY, Deng GT, Zeng FR. Bromodomain and extra-terminal inhibitors emerge as potential therapeutic avenues for gastrointestinal cancers. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022; 14(1): 75-89
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v14/i1/75.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v14.i1.75