Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Feb 15, 2020; 12(2): 149-172
Published online Feb 15, 2020. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i2.149
Published online Feb 15, 2020. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i2.149
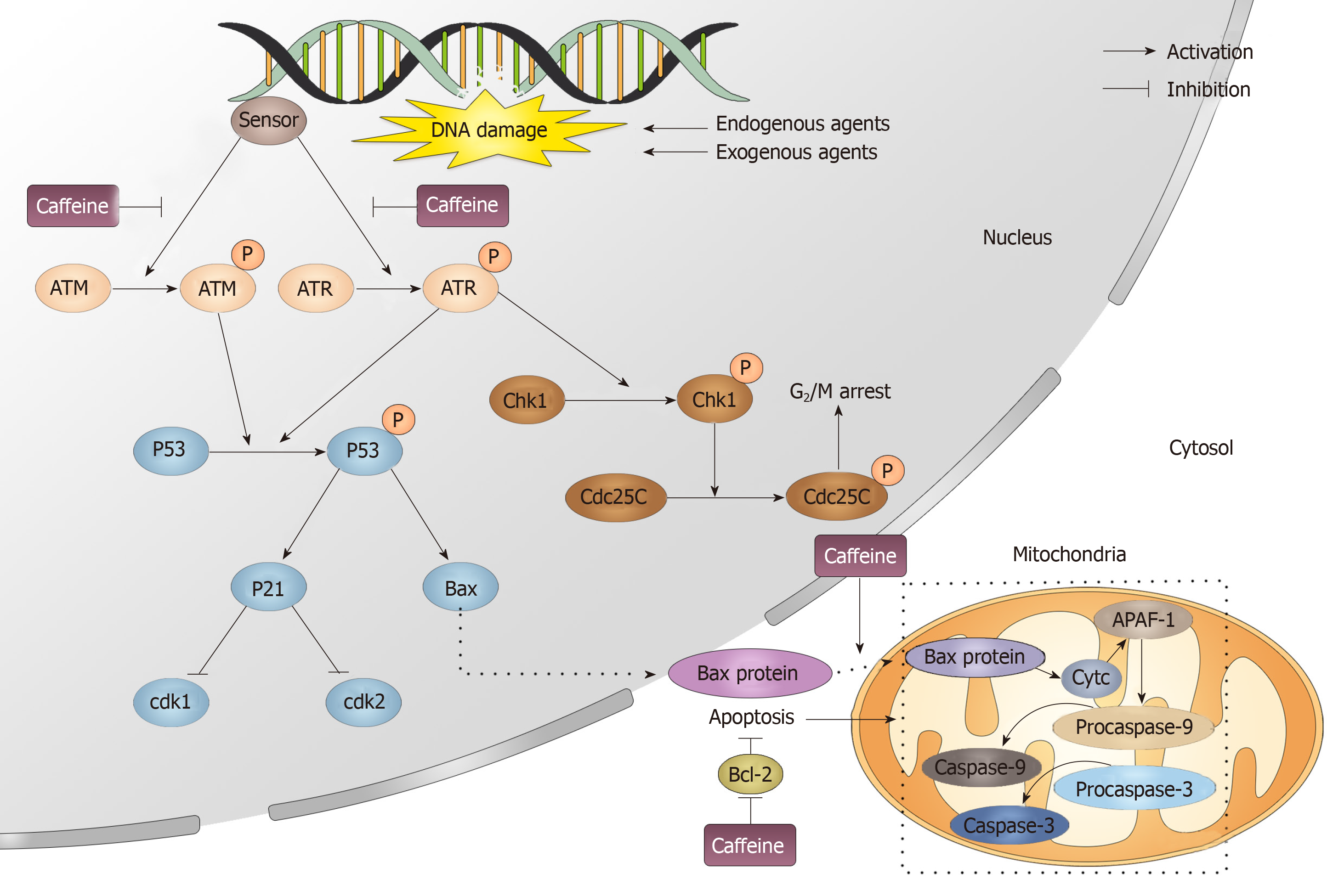
Figure 10 Caffeine influences the DNA repair process.
When exogenous and endogenous agents attack DNA, DNA can be damaged, which immediately activates the DNA repair process. In this process, a sensor detects the damage and then causes the phosphorylation of ataxia-telangiectasia mutated and ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related. Caffeine can inhibit the activation of both ataxia-telangiectasia mutated and ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related. Phosphorylated ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related and ataxia-telangiectasia mutated can activate cyclin-dependent kinase 1, which induces G2/M arrest and p53. p53 then modulates its downstream target p21, which can influence the cell cycle by inhibiting Cdk1 and Cdk2. Moreover, Bax is also downstream of p53, and when it enters the cytosol, it can initiate the apoptosis process. Caffeine can promote apoptosis by inhibiting the translocation of Bax from the nucleus to the mitochondria and also by promoting the apoptosis inhibitor Bcl-2. ATM: Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated; ATR: Ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related; Chk: Cyclin-dependent kinase.
- Citation: Cui WQ, Wang ST, Pan D, Chang B, Sang LX. Caffeine and its main targets of colorectal cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2020; 12(2): 149-172
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v12/i2/149.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v12.i2.149