Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Feb 15, 2020; 12(2): 149-172
Published online Feb 15, 2020. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i2.149
Published online Feb 15, 2020. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i2.149
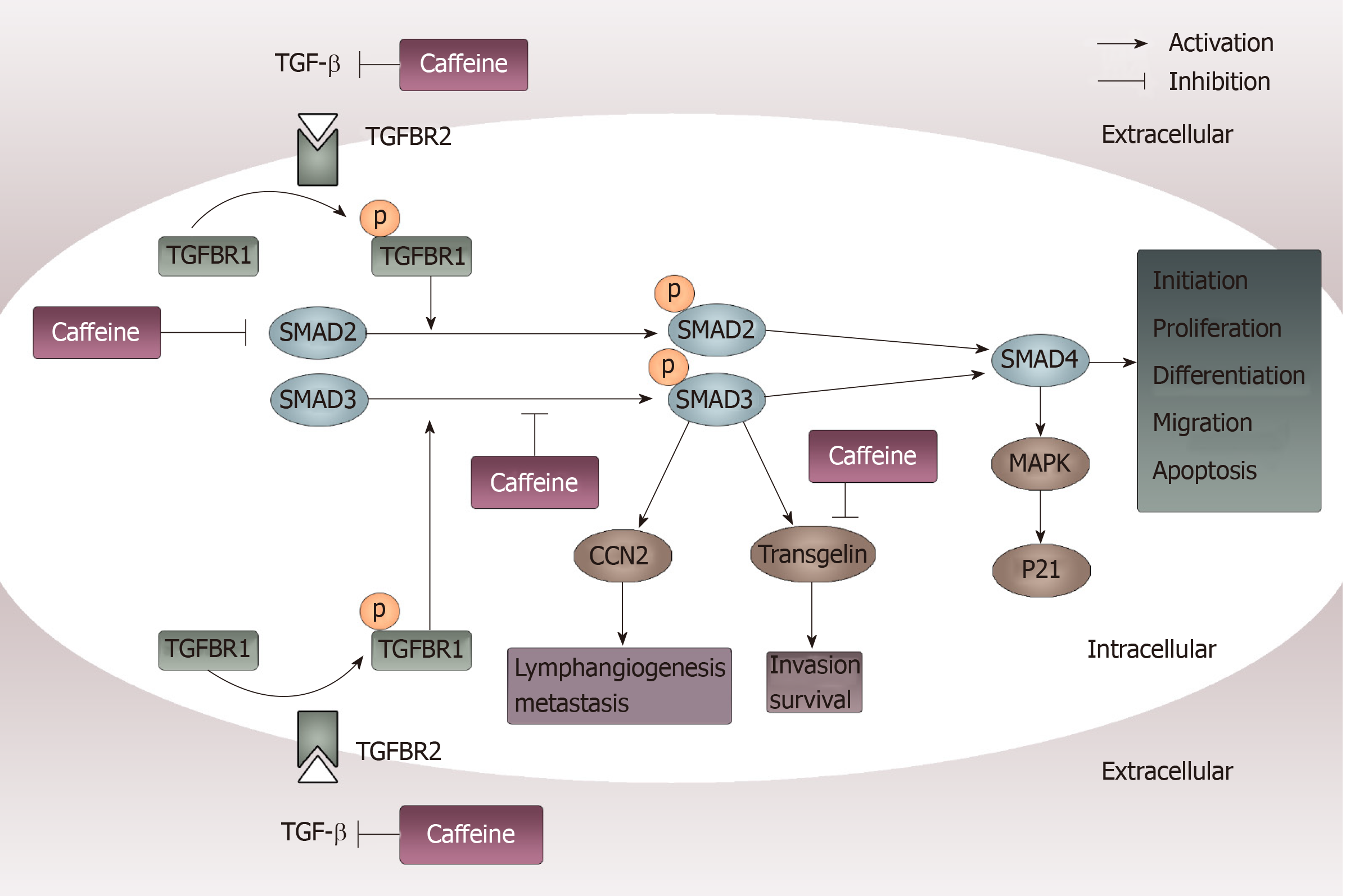
Figure 6 Inhibition of transforming growth factor β pathways caused by caffeine.
When transforming growth factor (TGF-β) acts on its type II receptor, the type I receptor can be recruited and phosphorylated. Then, mediated by the activated TGF-β type I receptor, SMAD2 and SMAD3 are phosphorylated and exert their functions by modulating downstream factors such as CCN-family protein 2 and transgelin or by binding to SMAD4. Caffeine may influence this pathway not only through inhibiting TGF-β at the beginning of the pathway but also by reducing the steady state concentration of total SMAD2 and decreasing phosphorylation of SMAD3. Furthermore, caffeine can directly inhibit transgelin, which plays an important part in invasion and survival. TGF-β: Transforming growth factor β; CCN2: CCN-family protein 2; TGFBR2: Transforming growth factor binding to the type II receptor; TGFBR1: Transforming growth factor binding to the type I receptor; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase.
- Citation: Cui WQ, Wang ST, Pan D, Chang B, Sang LX. Caffeine and its main targets of colorectal cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2020; 12(2): 149-172
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v12/i2/149.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v12.i2.149