Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Nov 15, 2020; 12(11): 1311-1324
Published online Nov 15, 2020. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i11.1311
Published online Nov 15, 2020. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i11.1311
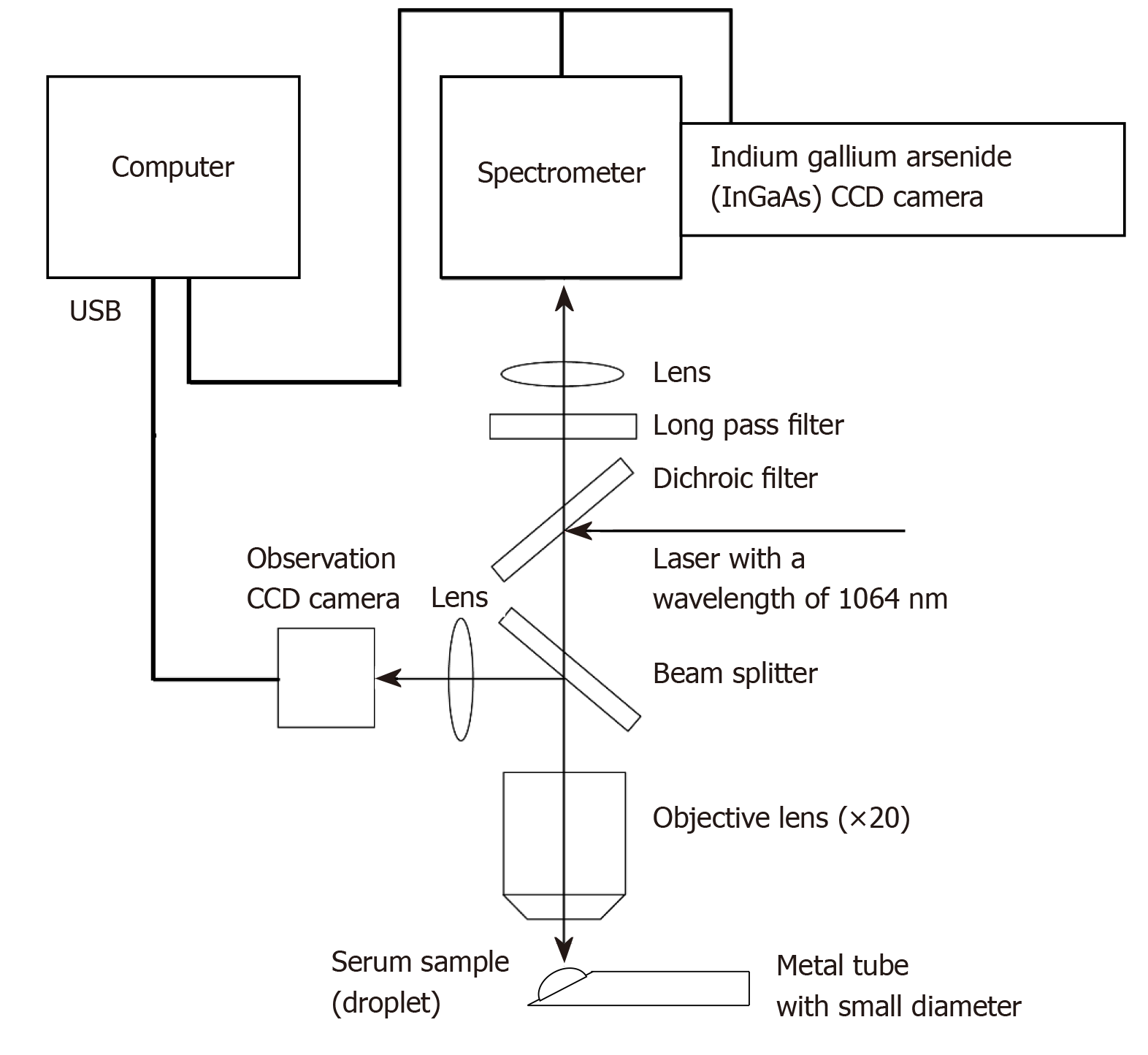
Figure 1 Schematic of the confocal micro-Raman spectrometer used in this study.
A nomadic Raman microscope with an excitation laser at a wavelength of 1064 nm was used in this study. A 20 × magnifying objective lens with a correction collar with near-infrared microscopy (LCPLN20XIR; Olympus Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) and a 2048 × 64 pixel thermoelectric cooled indium gallium arsenide (InGaAs), charge-couple device (CCD) detector, with a spectral range of 100-3200 cm-1 (grating 4 cm-1) were used to record the spectra.
- Citation: Ito H, Uragami N, Miyazaki T, Yang W, Issha K, Matsuo K, Kimura S, Arai Y, Tokunaga H, Okada S, Kawamura M, Yokoyama N, Kushima M, Inoue H, Fukagai T, Kamijo Y. Highly accurate colorectal cancer prediction model based on Raman spectroscopy using patient serum. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2020; 12(11): 1311-1324
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v12/i11/1311.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v12.i11.1311