Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Aug 15, 2019; 11(8): 599-621
Published online Aug 15, 2019. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i8.599
Published online Aug 15, 2019. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i8.599
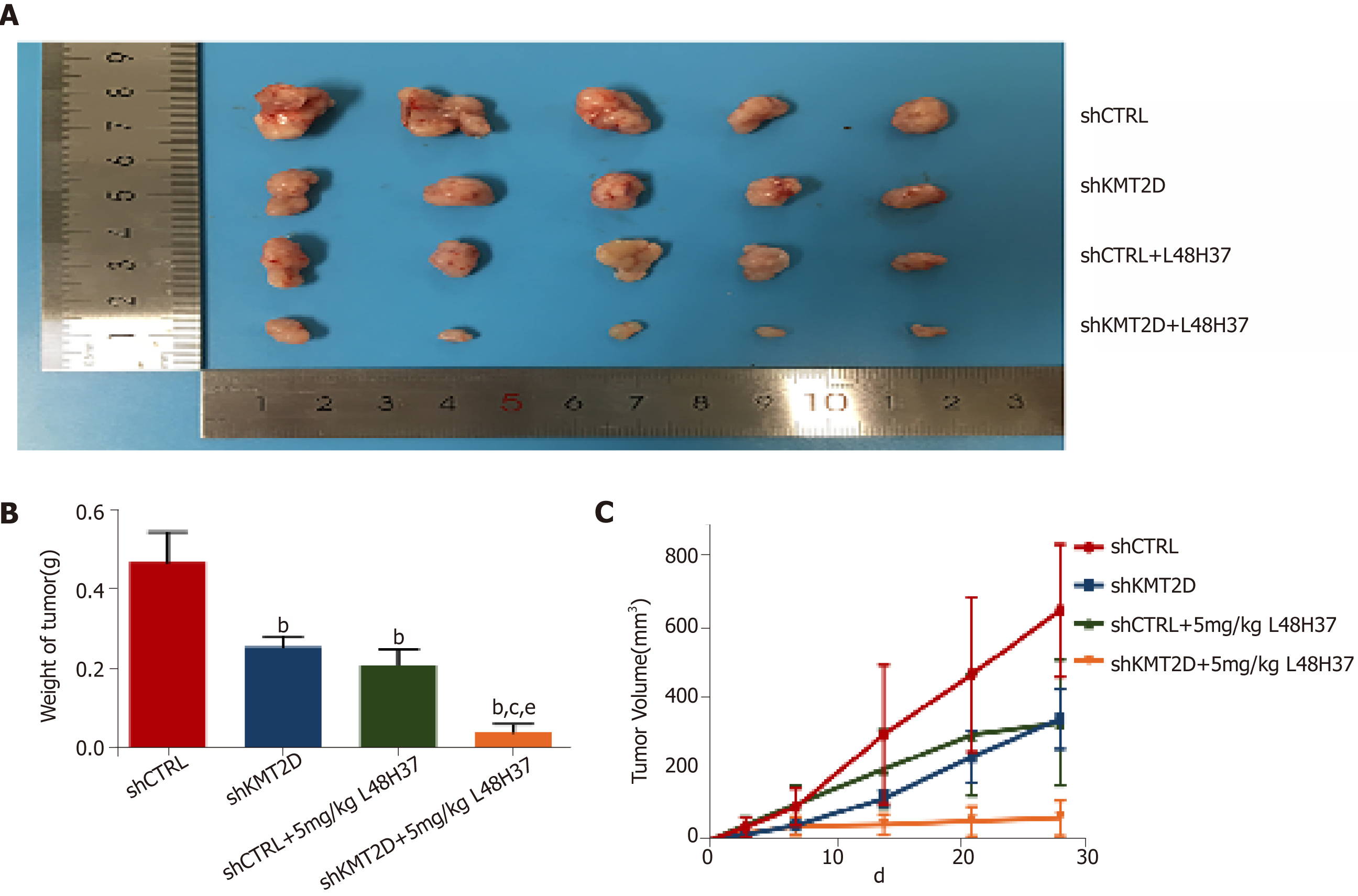
Figure 6 KMT2D knockdown synergizes with L48H37 to inhibit pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma xenograft growth in vivo.
A: The gross image of resected tumors; B: Effect of 5 mg/kg L48H37 treatment on wet tumor weight in relatively independent four sub-groups (shCTRL group, shKMT2D group, shCTRL + 5 mg/kg L48H37 group and shKMT2D + 5 mg/kg L48H37 group). Data were expressed as mean ± SEM. bP < 0.01 vs shCTRL group. cP < 0.05 vs shKMT2D group. eP < 0.05 vs shCTRL + 5 mg/kg L48H37 group; C: Tumor volumes recorded at different follow-up times in the above four sub-groups. Data were expressed as mean ± SEM. P < 0.01 (shCTRL group vs shKMT2D group; shCTRL group vs shCTRL + 5 mg/kg L48H37 group; shCTRL group vs shKMT2D + 5 mg/kg L48H37 group; shKMT2D group vs shKMT2D + 5 mg/kg L48H37 group; shCTRL + 5 mg/kg L48H37 group vs shKMT2D + 5 mg/kg L48H37 group).
- Citation: Li SS, Jiang WL, Xiao WQ, Li K, Zhang YF, Guo XY, Dai YQ, Zhao QY, Jiang MJ, Lu ZJ, Wan R. KMT2D deficiency enhances the anti-cancer activity of L48H37 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2019; 11(8): 599-621
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v11/i8/599.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v11.i8.599