Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Aug 15, 2019; 11(8): 599-621
Published online Aug 15, 2019. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i8.599
Published online Aug 15, 2019. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i8.599
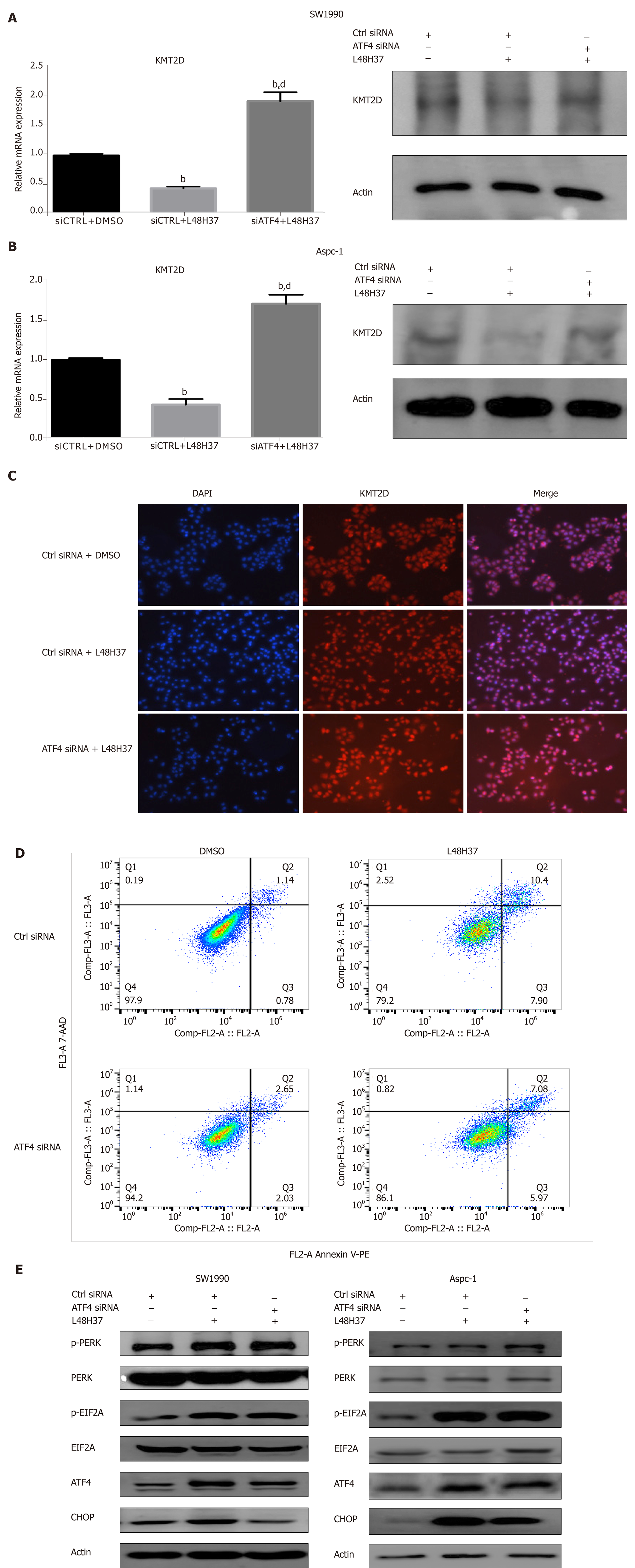
Figure 3 ATF-4 knockdown attenuates L48H37-induced apoptosis and upregulates KMT2D.
A, B: KMT2D mRNA and protein levels in the control and ATF-4-knockdown SW1990 and ASPC-1 cells treated with 15 µM L48H37 for 12 h. β-actin was used as an internal control. Data were expressed as mean ± SEM. bP < 0.01 vs siCTRL + DMSO group. dP < 0.01 vs siCTRL + L48H37 group; C: Representative IF image showing KMT2D expression in control and ATF4-knockdown SW1990 cells treated with L48H37; D: FACS plot showing apoptosis in control and ATF4 knockdown SW1990 cells treated with L48H37; E, F: Western blotting showing levels of p-PERK, PERK, p-EIF2α, EIF2α, ATF4 and CHOP in control and ATF4 knockdown SW1990 cells treated with L48H37. β-actin was used as an internal control. PERK: Protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; EIF2A: Eukaryotic initiation factor 2α; ATF-4: Activating transcription factor-4; CHOP: Enhancer-binding protein-homologous protein.
- Citation: Li SS, Jiang WL, Xiao WQ, Li K, Zhang YF, Guo XY, Dai YQ, Zhao QY, Jiang MJ, Lu ZJ, Wan R. KMT2D deficiency enhances the anti-cancer activity of L48H37 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2019; 11(8): 599-621
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v11/i8/599.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v11.i8.599