Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jun 15, 2019; 11(6): 449-458
Published online Jun 15, 2019. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i6.449
Published online Jun 15, 2019. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i6.449
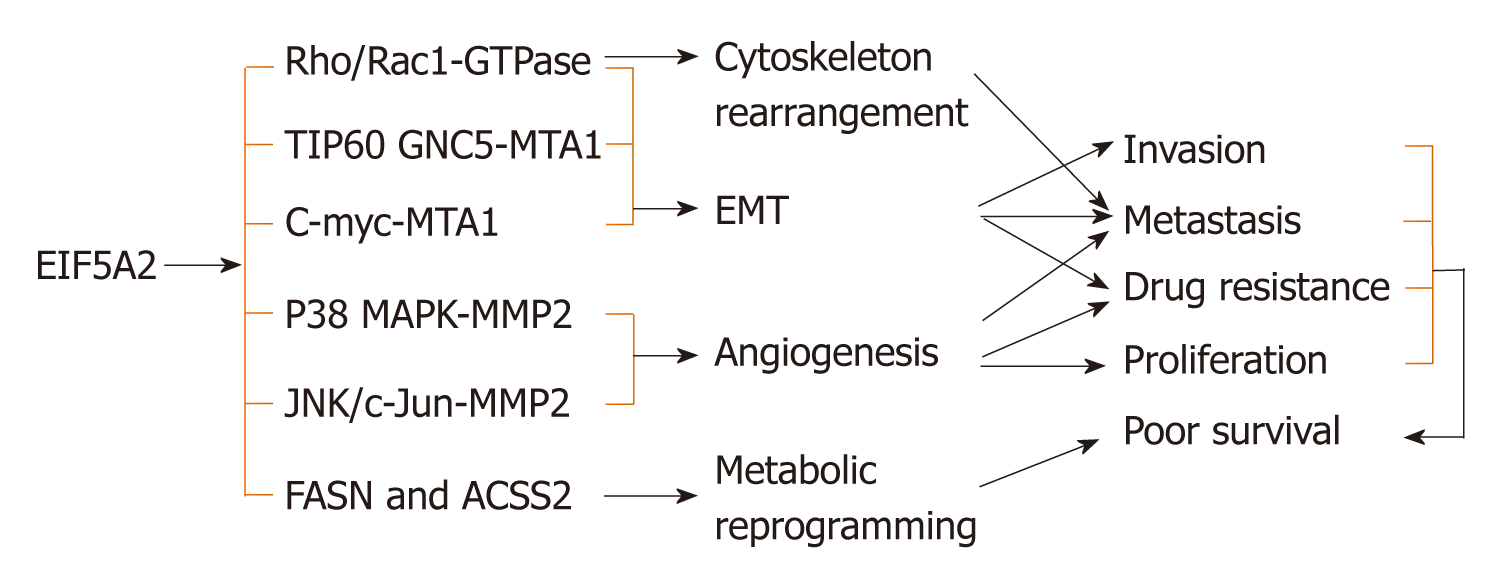
Figure 1 unctions and subsequent pathways of eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2 in human digestive system neoplasms.
Overexpression of Eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2 (eIF5A2) induces epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) by enhancing RhoA/Rac1-GTPase and ITP60 GNC5-MTA1 activity in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Overexpression of EIF5A2 also promotes colorectal carcinoma and gastric cancer cell aggressiveness by upregulating the C-myc/MTA axis to induce EMT. Increased expression of eIF5A2 contributes to angiogenesis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via the P38 MAPK/MMP2 pathway. eIF5A2 promotes cell proliferation and triggers cellular metabolic reprogramming in HCC cells, including glucose metabolism and fatty acid biosynthesis via upregulation of FASN and ACSS2. In HCC, eIF5A2 stimulates rearrangement of the cytoskeleton through activation of the RhoA/Rac1 GTPase signaling pathway. eIF5A2: Eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2; EMT: Epithelial–mesenchymal transition.
- Citation: Meng QB, Peng JJ, Qu ZW, Zhu XM, Wen Z, Kang WM. Eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2 and human digestive system neoplasms. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2019; 11(6): 449-458
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v11/i6/449.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v11.i6.449