Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Sep 15, 2018; 10(9): 244-259
Published online Sep 15, 2018. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v10.i9.244
Published online Sep 15, 2018. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v10.i9.244
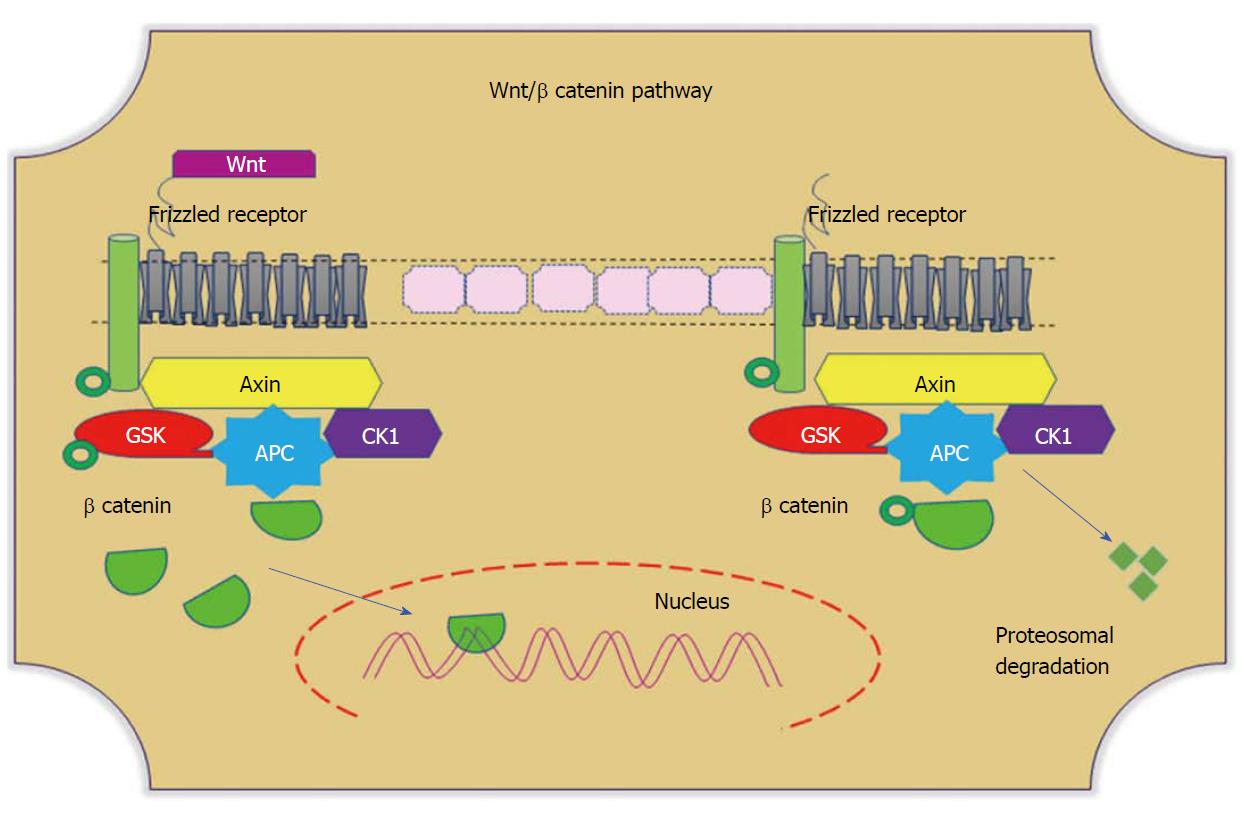
Figure 4 Wnt/β-catenin pathways.
In the absence of Wnt, cytoplasmic β-catenin forms a complex with Axin (yellow), APC (blue), GSK3 (red), and CK1 (purple). Phosphorylated β-catenin undergoes ubiquitin-mediated proteosomal degradation. In the presence of Wnt, Wnt binds to the frizzled receptor, which in turn recruits the Axin complex. This disrupts Axin-mediated proteosomal degradation of β-catenin. Cytoplasmic β-catenin then travels to the nucleus and functions as a co-activator with TCF to activate Wnt-regulated gene expression. GSK: Glycogen synthase kinase; APC: Adenomatous polyposis coli; CK1: Casein kinase 1.
- Citation: Pandurangan AK, Divya T, Kumar K, Dineshbabu V, Velavan B, Sudhandiran G. Colorectal carcinogenesis: Insights into the cell death and signal transduction pathways: A review. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2018; 10(9): 244-259
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v10/i9/244.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v10.i9.244