Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Jan 25, 2016; 8(2): 86-103
Published online Jan 25, 2016. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v8.i2.86
Published online Jan 25, 2016. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v8.i2.86
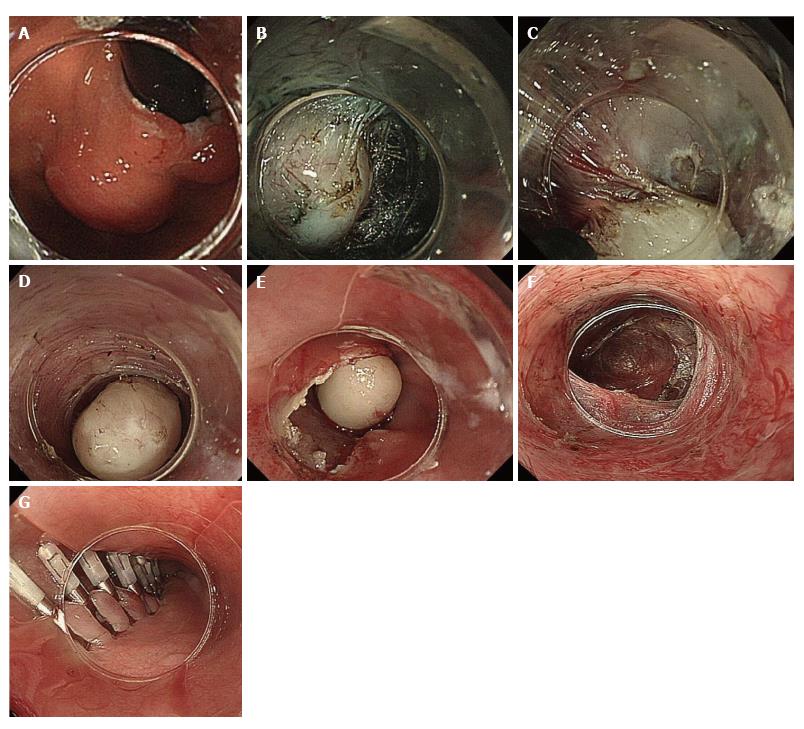
Figure 3 Schema of stages of peroral endoscopic tumor resection.
A: Gastric cardia SMT in retroversion view; B: Submucosal tunneling. After initial mucosal incision approximately 5 cm proximal to the edge of the SMT, saline and indigo carmine are injected to create a mucosal bleb. A submucosal tunnel is created by dissecting the submucosal fibers. Submucosal dissection is advanced beyond the distal tumor edge; C: Tumor excision. The submucosal tumor is dissected from the muscle layer. All muscle bundles that connect to the submucosal tumor are cut with the triangle-tip knife; D and E: Removal of the submucosal tumor. The totally mobilized tumor is extracted from the submucosal space (D) through the mucosal incision (E). The submucosal tumor is caught tightly by endoscopic suction at the tip of its distal attachment. Submucosal tumors generally have an oval shape, which enables smooth removal out through the mucosal entry; F: Submucosal tunnel after removal of SMT; G: Closure of the mucosal entry incision. After confirmation of complete hemostasis in the submucosal tunnel (F), the mucosal entry is tightly closed with hemostatic clips. POET: Peroral endoscopic tumor resection; SMT: Submucosal tumor.
- Citation: Eleftheriadis N, Inoue H, Ikeda H, Onimaru M, Maselli R, Santi G. Submucosal tunnel endoscopy: Peroral endoscopic myotomy and peroral endoscopic tumor resection. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2016; 8(2): 86-103
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v8/i2/86.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v8.i2.86