Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Jan 25, 2016; 8(2): 86-103
Published online Jan 25, 2016. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v8.i2.86
Published online Jan 25, 2016. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v8.i2.86
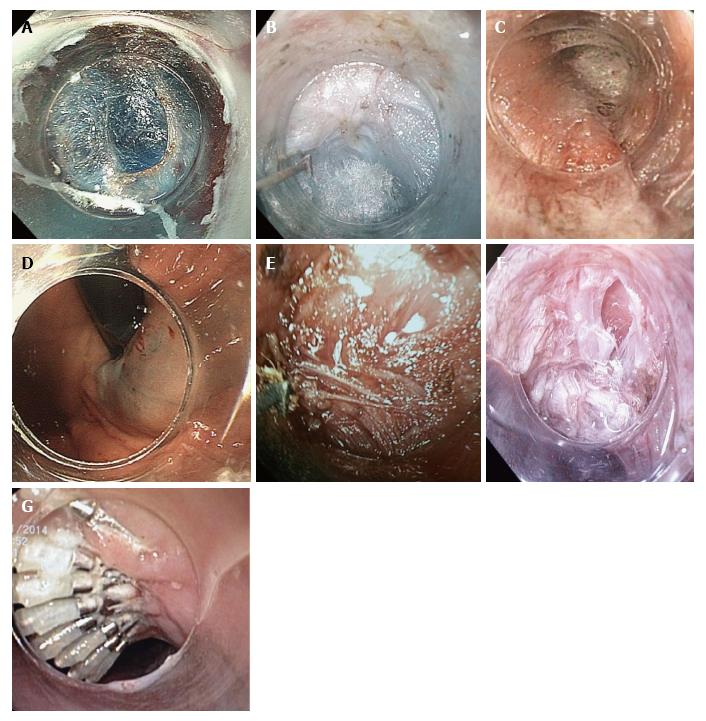
Figure 1 Peroral endoscopic myotomy stages.
A: Mucosal entry after longitudinal incision at the 2-o’clock position; B: Submucosal tunneling. Ectopic innermost longitudinal muscle bundles in front of the circular muscle layer are recognized; C: Palisade vessels at the EGJ inside the tunnel; D: Blue dye at retroversion in the stomach confirms tunnel extension to gastric side; E: The sharp tip of the TT-knife is used to catch circular muscle bundles and then retract them toward the esophageal lumen; F: Longitudinal muscle is identified at the bottom of myotomy site. Longitudinal muscle fibers split each other and a gap is recognized, creating an unintentional, partly full-thickness myotomy; G: Mucosal closure with endoscopic clips. EGJ: Esophagogastric junction.
- Citation: Eleftheriadis N, Inoue H, Ikeda H, Onimaru M, Maselli R, Santi G. Submucosal tunnel endoscopy: Peroral endoscopic myotomy and peroral endoscopic tumor resection. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2016; 8(2): 86-103
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v8/i2/86.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v8.i2.86