Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Nov 16, 2016; 8(19): 690-696
Published online Nov 16, 2016. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v8.i19.690
Published online Nov 16, 2016. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v8.i19.690
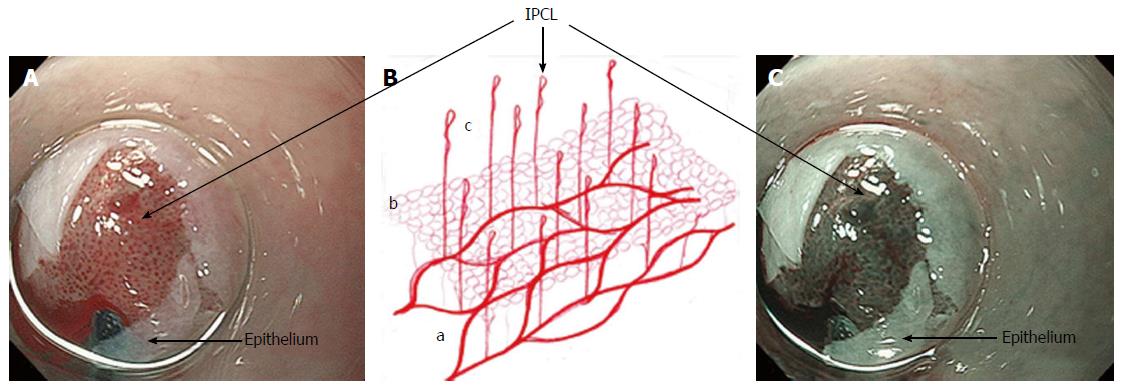
Figure 1 Mucosal vessels.
A and C: Endoscopic images during per-oral endoscopic myotomy procedure (high magnification images); after unintentional removal of the epithelium (white layer), top half of epithelium was peeled off, and IPCLs were exposed. IPCLs appear as regularly-arranged, red dots (A: White light) or dark green spots (C: NBI); B: A schematic representation of the vascular network of esophageal mucosa: a: Branching vessels; b: SECN; c: IPCL. IPCL: Intrapapillary capillary loop; SECN: Sub epithelial capillary network; NBI: Narrow band imaging.
- Citation: Maselli R, Inoue H, Ikeda H, Onimaru M, Yoshida A, Santi EG, Sato H, Hayee B, Kudo SE. Microvasculature of the esophagus and gastroesophageal junction: Lesson learned from submucosal endoscopy. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2016; 8(19): 690-696
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v8/i19/690.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v8.i19.690