Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Jul 25, 2015; 7(9): 860-871
Published online Jul 25, 2015. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i9.860
Published online Jul 25, 2015. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i9.860
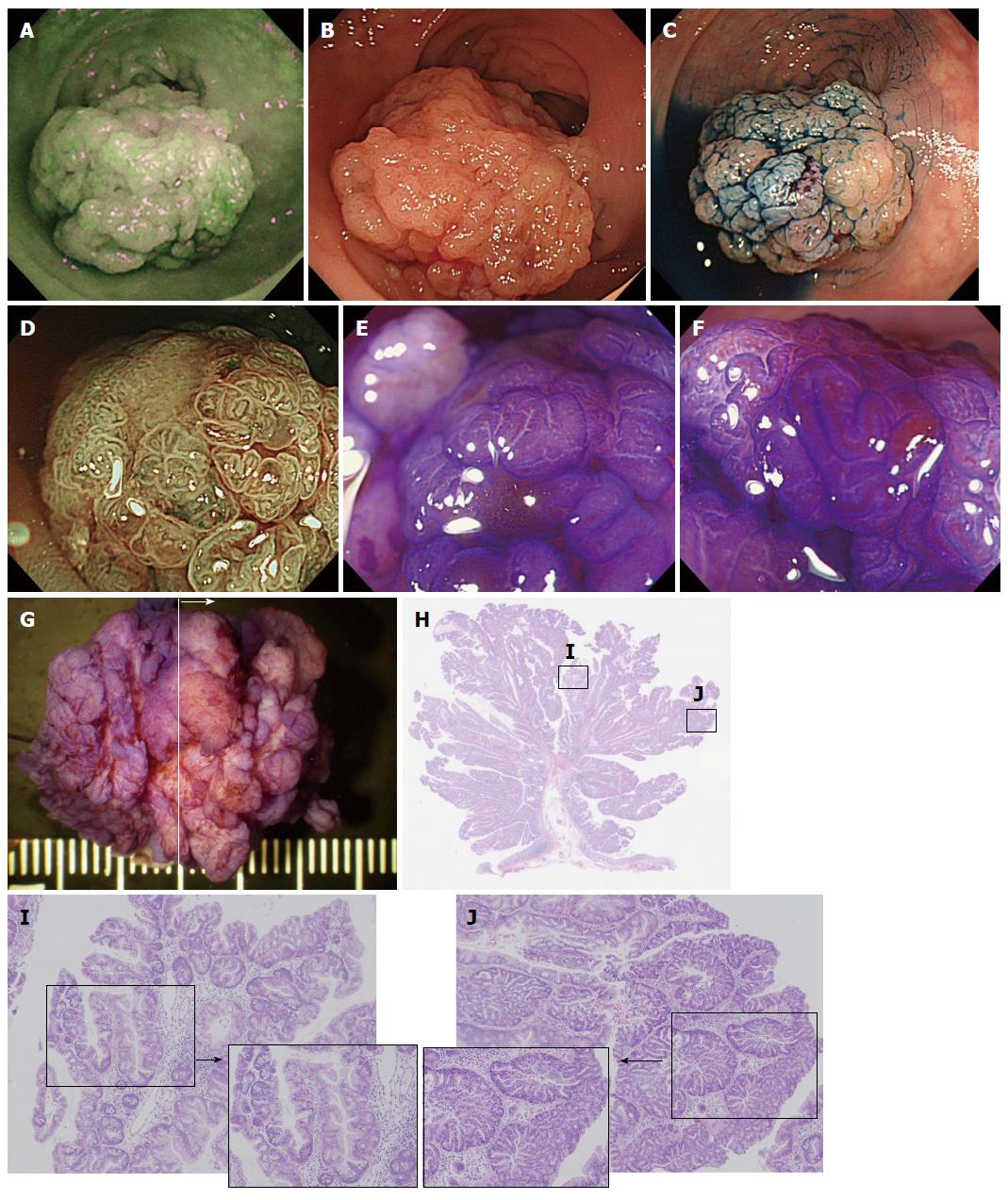
Figure 5 A case of a traditional serrated adenoma with conventional dysplasia (scope: CF: FH260AZI).
A: AFI imaging. A dark green tone that is nearly the same as the surrounding normal colon mucosa can be observed in the tumor; B: Conventional white light observation. A large (approximately 30 mm) semipedunculated polyp exhibiting a slightly reddish change can be observed at the rect-sigmoid junction. There are no findings suggestive of submucosal invasion of the cancer; C: Indigocarmine spraying endoscopic findings. The structure of the nodular surface pattern is clearly revealed; D: NBI observation, magnified. A granular surface pattern with dilated microcapillary vessels can be observed in the tumor; E and F: Magnified crystal violet staining with observation. A type IIIH or IVH pit pattern is shown in the tumor; G: Stereoscopic finding. The tumor was excised by the EMR method. The tumor was cut into 4 pieces; H: HE staining, whole specimen finding from section #2; I: Histological findings from the HE staining. The tumor contains serrated glands in the mucosal layer. Dysplastic change is not observed; J: Histological findings of the HE staining. At several points, TSAs with conventional epithelial dysplasia exhibiting enlarged crowding and pseudostratification of the nuclei with crypt structure dysplastic changes can be observed. TSA: Traditional serrated adenoma; NBI: Narrow band imaging; AFI: Auto fluorescence imaging.
- Citation: Saito S, Tajiri H, Ikegami M. Serrated polyps of the colon and rectum: Endoscopic features including image enhanced endoscopy. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2015; 7(9): 860-871
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v7/i9/860.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v7.i9.860