Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Oct 25, 2015; 7(15): 1170-1180
Published online Oct 25, 2015. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i15.1170
Published online Oct 25, 2015. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i15.1170
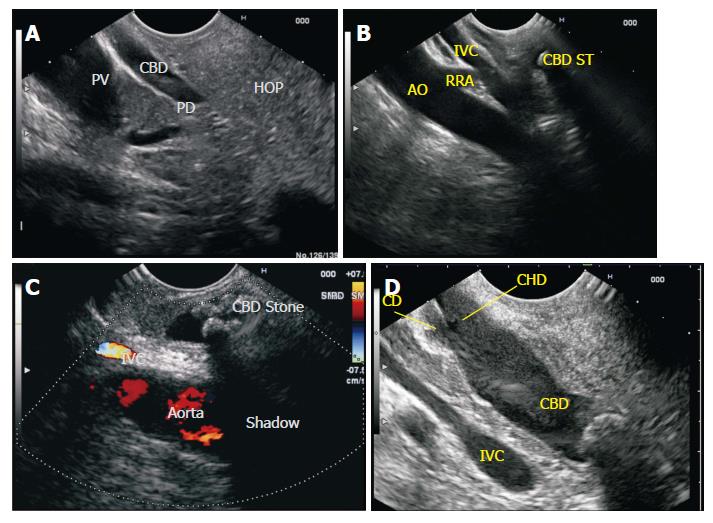
Figure 7 Common bile duct Imaging from duodenal bulb.
A: The portal vein is identified as the home based position from duodenal bulb. From the home base position a limited range of movement of 90 degree to either side traces the entire CBD. A clockwise rotation traces the CBD towards the ampulla and identifies the middle and lower 1/3 of CBD and anticlockwise rotation traces the CBD towards the upper 1/3 and the GB/CD/CHD are also identified near the liver hilum. In this image the CBD is seen in a long axis for a long distance and the PD and portal vein are seen in a long axis for a short distance. This has been called as reverse stack sign; B: In this figure the stack of bile duct (with a stone) aorta and IVC is seen from duodenal bulb. The right renal artery is seen going behind the IVC. The CBD in this case lies in the retropancreatic part anterior to IVC; C: Two stones are seen in the path of acoustic shadow. Although both stones have same acoustic impedance yet it is the second stone, which is causing acoustic shadow. The second stone is surrounded by fluid and the sound waves go through acoustic medium of different acoustic impedance; D: The pyramidal shaped neck of pancreas and pancreatic duct are commonly identified between the probe and portal vein. CBD: Common bile duct; CHD: Common hepatic duct; IVC: Inferior venacava; PV: Portal vein; PD: Pancreatic duct; HOP: Head of pancreas; RRA: Right renal artery; AO: Aorta.
- Citation: Sharma M, Pathak A, Shoukat A, Rameshbabu CS, Ajmera A, Wani ZA, Rai P. Imaging of common bile duct by linear endoscopic ultrasound. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2015; 7(15): 1170-1180
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v7/i15/1170.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v7.i15.1170