Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Oct 25, 2015; 7(15): 1170-1180
Published online Oct 25, 2015. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i15.1170
Published online Oct 25, 2015. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i15.1170
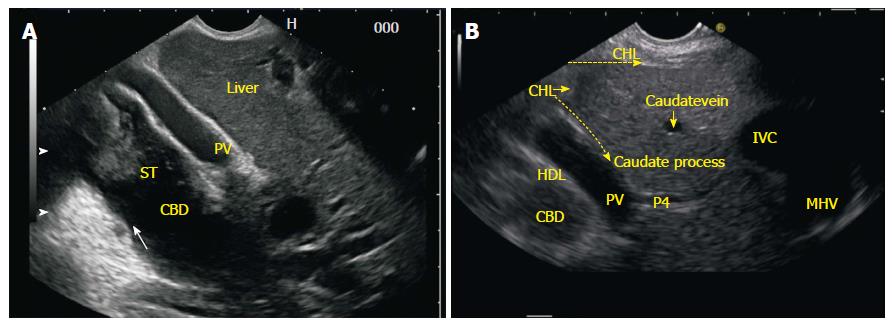
Figure 4 Common bile duct as seen from the gastroesophageal junction.
A: A clockwise rotation moves the axis of imaging from an anterior position in stomach to a lateral position where the liver hilum is placed and follows the segmental duct towards the confluence of both the right and left hepatic ducts; B: In this figure the two limbs of GHL are seen. One of the limb runs on the under surface of liver and the other limb goes in the area between abdominal part of esophagus and liver. As the rotation is executed the presence of hyperchaotic GHL between esophagus and liver and the hepatoduodenal ligament near the liver hilum may interfere with imaging of part of the left or right hepatic ducts near the confluence. CHD: Common hepatic duct; IVC: Inferior venacava; HDL: Hepatoduodenal ligament; IVC: Inferior venacava; GHL: Gastrohepatic ligament.
- Citation: Sharma M, Pathak A, Shoukat A, Rameshbabu CS, Ajmera A, Wani ZA, Rai P. Imaging of common bile duct by linear endoscopic ultrasound. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2015; 7(15): 1170-1180
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v7/i15/1170.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v7.i15.1170