Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Sep 10, 2015; 7(12): 1070-1077
Published online Sep 10, 2015. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i12.1070
Published online Sep 10, 2015. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i12.1070
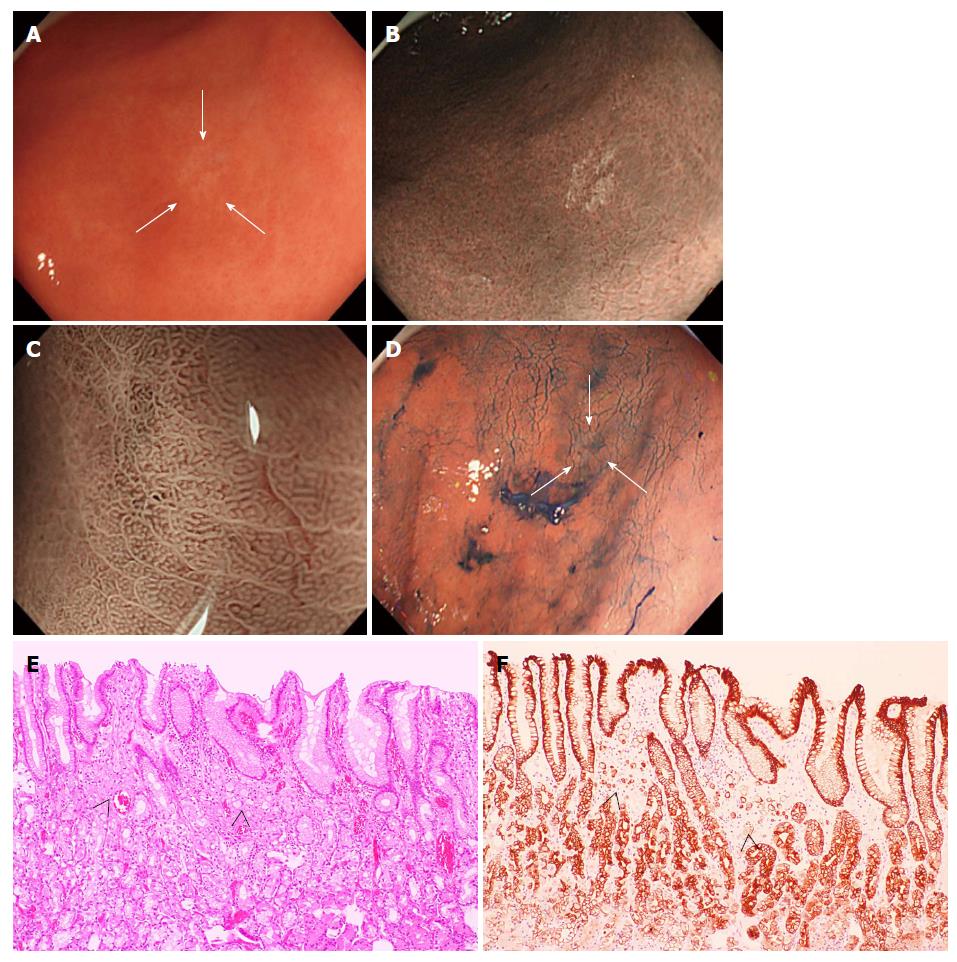
Figure 3 Endoscopic and microscopic images of signet ring cell carcinoma (Case 9).
A: Endoscopy with WLI revealed a 0-IIb lesion with slight discoloration (arrows) at the greater curvature of the angulus; B: NM-NBI of the cancer area showed an isolated clear whitish area. The cancerous areas were more clearly captured by NM-NBI endoscopy than by WLI endoscopy. The NBI and WLI index were respectively 25.6 and 12.8, and the C-index was 0.77; C and D: The demarcation line of the SRC was not clearly identified even by magnifying NBI and chromoendoscopy (arrows); E: The histology of a specimen resected by endoscopic submucosal dissection revealed an intramucosal SRC (arrowheads) in the upper third of the mucosa beneath a preserved surface epithelium; F: SRC cells showed positive for cytokeratin AE1/AE3 staining (arrowheads). WLI: White-light imaging; NM-NBI: Non-magnifying narrow-band imaging; SRC: Signet ring cell carcinoma.
- Citation: Watari J, Tomita T, Ikehara H, Taki M, Ogawa T, Yamasaki T, Kondo T, Toyoshima F, Sakurai J, Kono T, Tozawa K, Ohda Y, Oshima T, Fukui H, Hirota S, Miwa H. Diagnosis of small intramucosal signet ring cell carcinoma of the stomach by non-magnifying narrow-band imaging: A pilot study. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2015; 7(12): 1070-1077
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v7/i12/1070.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v7.i12.1070