Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Jun 16, 2014; 6(6): 240-247
Published online Jun 16, 2014. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v6.i6.240
Published online Jun 16, 2014. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v6.i6.240
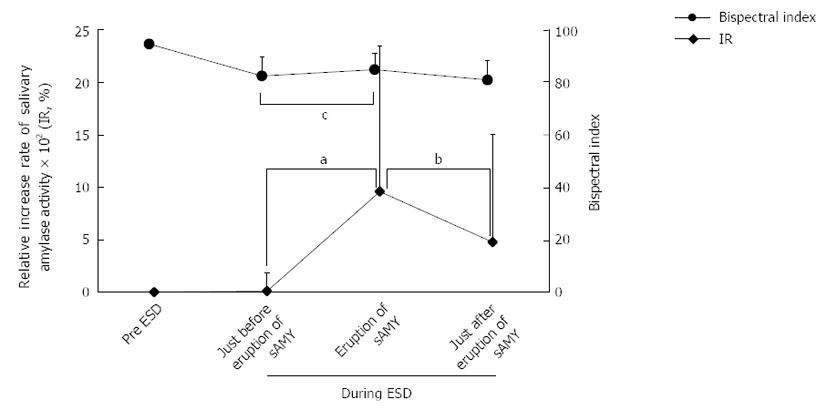
Figure 1 Changes in the relative rate of increase of the salivary amylase activity level compared with the control level, salivary amylase activity (IR, %), and the bispectral index around the 26 episodes of salivary amylase activity elevation in the H-group.
The baseline level of sAMY significantly increased in association with an IR of > 100% at only 5 min, with a significant difference (IR immediately before elevation/IR at elevation of sAMY = 8.72 ± 173/958 ± 1391%, aP < 0.001). However, the release of gastric wall tension and/or pentazocine injection effectively decreased the elevated sAMY level immediately within only 5 min with a significant difference (IR at sAMY elevation/immediately after intervention = 958 ± 1391/476 ± 1031, bP < 0.001). The bispectral indices in the patients undergoing ESD proved to be stable throughout the procedures (cP = 0.272), even when the sAMY level was elevated in association with an IR of > 100%, i.e., when the patient received SE. All 14 patients responded with “I did not wake up at all” on the post-ESD questionnaire. The data are presented as the mean ± SD. ESD: Endoscopic submucosal dissection; DS: Deep sedation; sAMY: Salivary amylase activity; SE: Sympathetic excitement; H-sAMY: A high value of salivary amylase activity; L-sAMY: A low value of salivary amylase activity.
- Citation: Uesato M, Nabeya Y, Akai T, Inoue M, Watanabe Y, Horibe D, Kawahira H, Hayashi H, Matsubara H. Monitoring salivary amylase activity is useful for providing timely analgesia under sedation. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2014; 6(6): 240-247
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v6/i6/240.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v6.i6.240