Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Dec 16, 2014; 6(12): 592-599
Published online Dec 16, 2014. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v6.i12.592
Published online Dec 16, 2014. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v6.i12.592
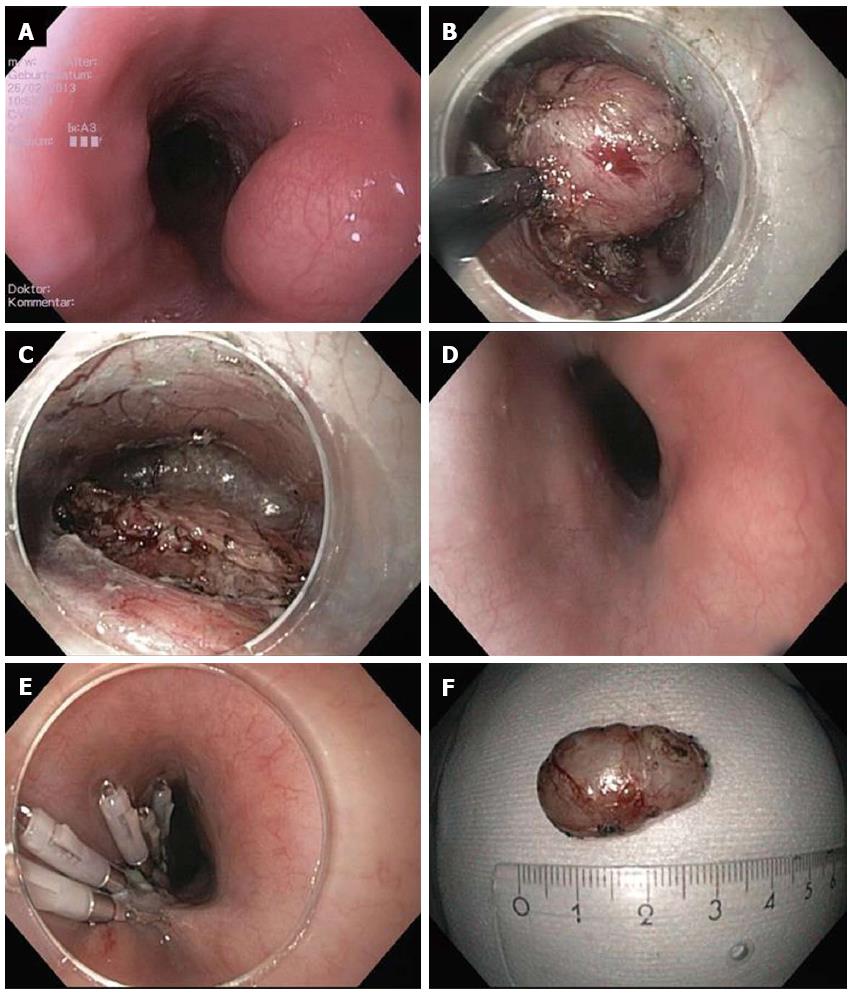
Figure 1 Submucosal endoscopic tumor resection/tunneling technique.
A: Endoscopic image of lumen obstruction subepithelial tumor in the proximal esophagus in a 42 years old woman with dysphagia; B: After preparing the submucosal tunnel, the tumor gets visible and is enucleated in endoscopic submucosal dissection-technique with a TT knife. The tumor was arising from the muscularis propria; C: Resection site (endoscope in the submucosal tunnel). The muscularis propria is excised/perforated; D: Resection site (endoscope in the esophageal lumen. Intact mucosa completely covers the muscular perforation; E: The mucosal incision (about 5 cm proximal tot he resection site) was closed with standard clips; F: Resection specimen. Histological examination revealed a Leiomyoma, which had been R0-resected.
- Citation: Schmidt A, Bauder M, Riecken B, Caca K. Endoscopic resection of subepithelial tumors. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2014; 6(12): 592-599
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v6/i12/592.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v6.i12.592