Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Apr 16, 2013; 5(4): 191-196
Published online Apr 16, 2013. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v5.i4.191
Published online Apr 16, 2013. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v5.i4.191
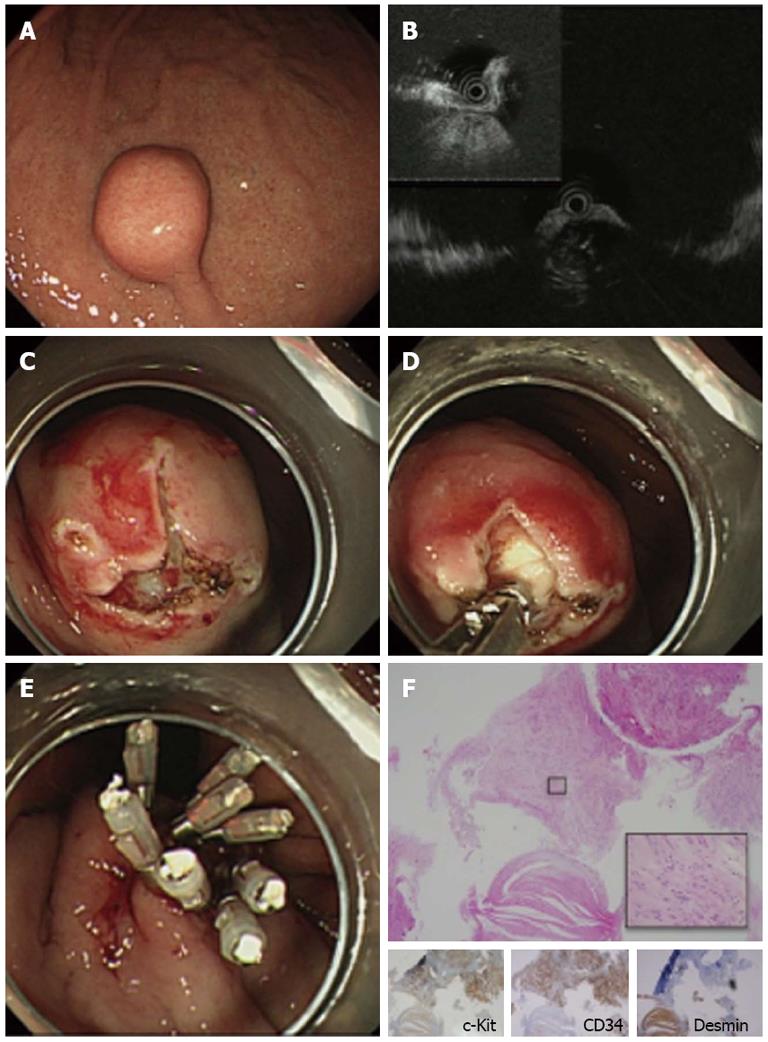
Figure 1 Case 1 of gastrointestinal stromal tumor which underwent mucosal incision assisted biopsy.
A: Endoscopic image of the lesion. The lesion was covered by normal mucosa with a bridging fold; B: Endoscopic ultrasonography imaging of the lesion with a miniature probe. The lesion was located in the 4th layer (muscularis propria); C: Two mucosal incisions were made to expose a portion of the lesion; D: Tissue samples were obtained using biopsy forceps; E: Closure of the mucosal incisions with endoclips; F: Pathological examination of the biopsied specimen. Immunohistochemical analysis showed that the lesion was positive for c-Kit and CD34 and negative for desmin. The biopsy samples also contained normal smooth muscle tissue, which was negative for c-Kit and CD34 and positive for desmin.
- Citation: Ihara E, Matsuzaka H, Honda K, Hata Y, Sumida Y, Akiho H, Misawa T, Toyoshima S, Chijiiwa Y, Nakamura K, Takayanagi R. Mucosal-incision assisted biopsy for suspected gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumors. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2013; 5(4): 191-196
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v5/i4/191.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v5.i4.191