Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Oct 16, 2013; 5(10): 514-518
Published online Oct 16, 2013. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v5.i10.514
Published online Oct 16, 2013. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v5.i10.514
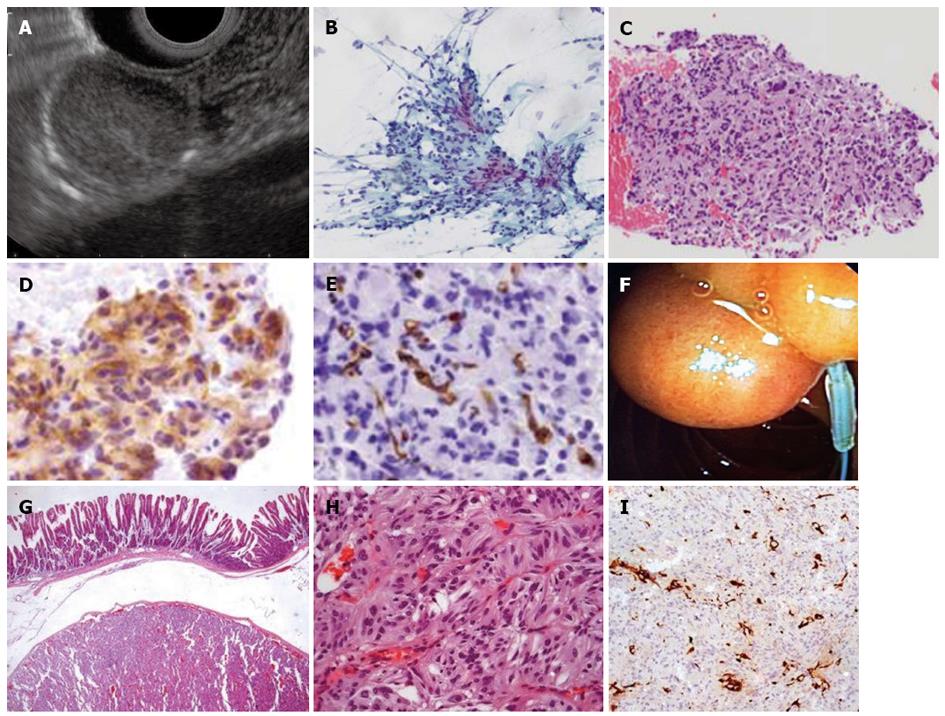
Figure 4 Endoscopic, endoscopic ultrasonography and pathological findings of gangliocytic paraganglioma.
A: Slightly hyperechoic lesion of the third layer of the duodenal wall; B-E: Endoscopic ultrasonography-fine needle aspiration with cytological features suggestive of GIST; B: Few fragments of loose mesenchymal spindle cell tissue fragments (Papanicolaou staining × 100); C: Cell block preparation of aspirated material, discrete nuclear atypia [Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) × 100]; D: Most cells stain positive for CD117 (× 400); E: Rare cells stained with CD34 (× 400); F: Resection of the subepithelial lesion using endoloop; G-I: Histopathological analysis of the resected tumor; G: Duodenal gangliocytic paraganglioma (HE × 25); H: Duodenal gangliocytic paraganglioma (HE × 200); I: Sustentacular S-100 positive cells documented (S100 ×100). GIST: Gastrointestinal stromal tumor.
- Citation: Figueiredo PC, Pinto-Marques P, Mendonça E, Oliveira P, Brito M, Serra D. Duodenal subepithelial hyperechoic lesions of the third layer: Not always a lipoma. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2013; 5(10): 514-518
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v5/i10/514.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v5.i10.514