Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Jun 16, 2010; 2(6): 193-197
Published online Jun 16, 2010. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v2.i6.193
Published online Jun 16, 2010. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v2.i6.193
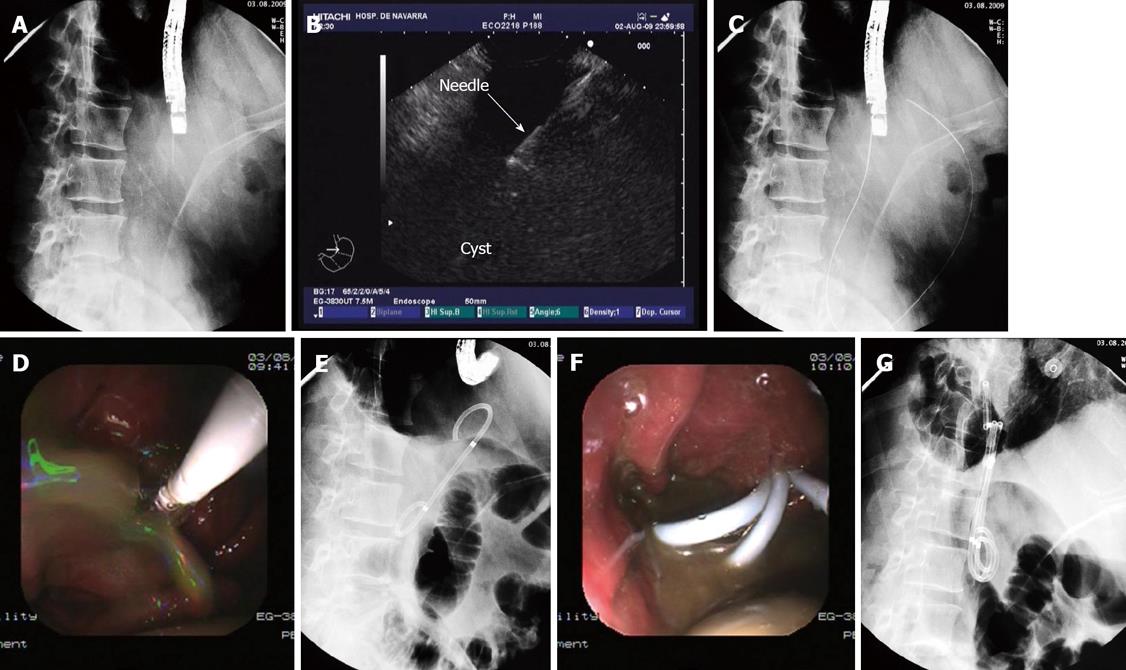
Figure 2 Approach to drain the pseudocyst.
A: In this fluoroscopic image the linear array echoendoscope is inside the gastric lumen in a stable and straightened position, with the needle coming out of the working channel; B: EUS image with linear array echoendoscope in which the needle can be seen inside the cyst once the puncture has been made; C: The guidewire is inserted through the needle and curled inside the cyst cavity; D: With deflation of the balloon dilator the pseudocyst contents spurts through the fistula into the gastric lumen; E: Fluoroscopic view of the first double pigtail stent inserted through the fistula connecting the gastric lumen and the cyst cavity (Dimensions of the stent: 5 cm long and 10 F diameter); F: Three double pigtail stents can be seen draining the cyst contents into the gastric lumen; G: The three double pigtail stents are placed transmurally. The gastric and cyst lumen can easily be seen on the X-ray image.
- Citation: Vila JJ, Carral D, Fernández-Urien I. Pancreatic pseudocyst drainage guided by endoscopic ultrasound. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2010; 2(6): 193-197
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v2/i6/193.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v2.i6.193