Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Dec 16, 2024; 16(12): 647-660
Published online Dec 16, 2024. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v16.i12.647
Published online Dec 16, 2024. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v16.i12.647
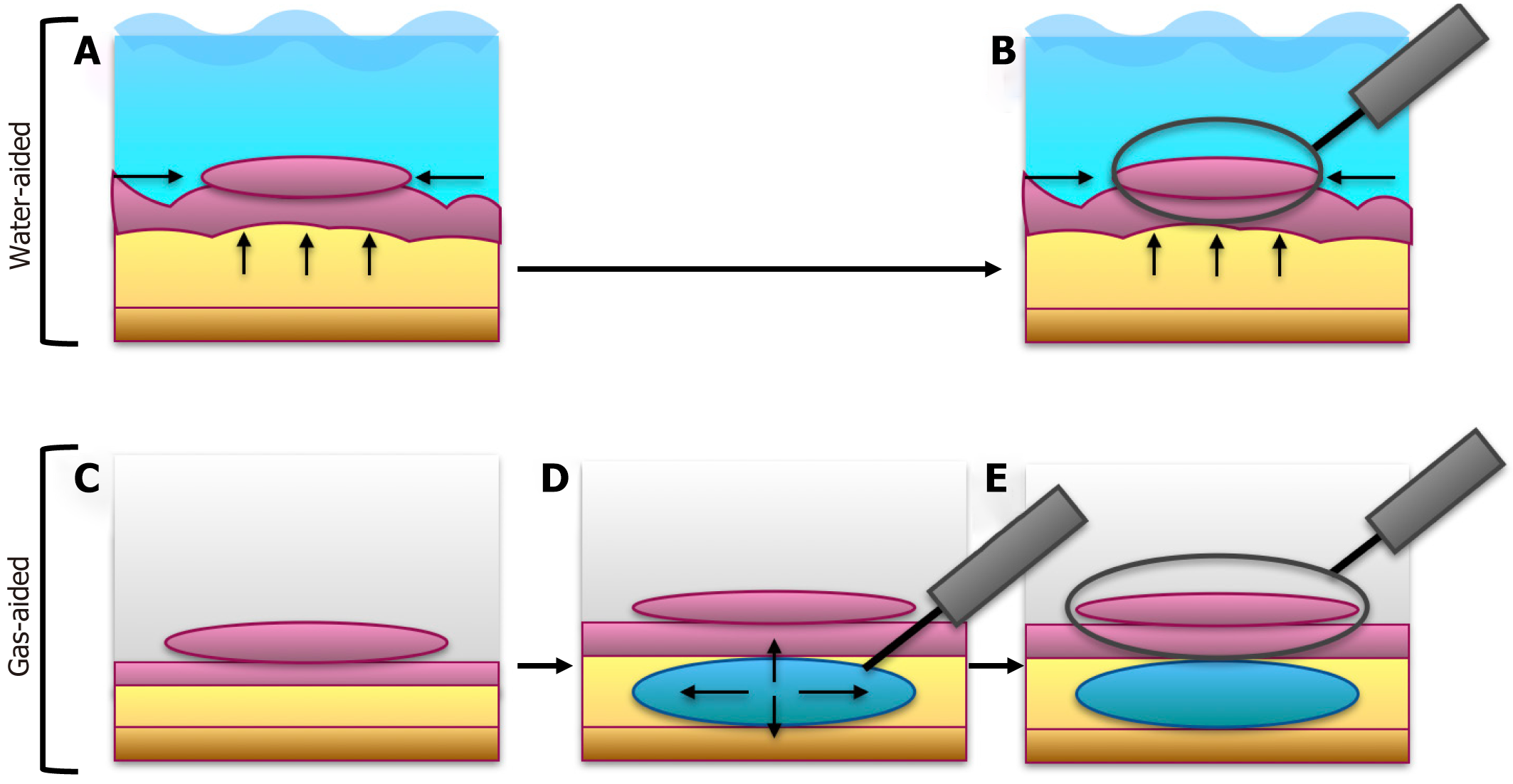
Figure 4 Advantages of water-aided colonoscopy in colonic mucosal lesion resections.
A: In the water-aided technique (upper portion of the figure), the introduction of water into the colon lumen allows for de-tensioning of the colonic walls and elevation of the mucosa (in pink) and submucosa (in yellow); B: This facilitates the removal of the mucosal lesion, as in an endoscopic mucosal resection using a snare; C: Conversely, in the gas-aided technique (lower portion of the figure), this elevating effect is absent, and the tension of the colonic walls is increased, resulting in reduced thickness of the mucosa and submucosa; D and E: Consequently, the submucosa must be elevated by injecting substances (e.g., diluted adrenaline in saline solution (D), to enable mucosal resection (E).
- Citation: Pellegrino R, Palladino G, Izzo M, De Costanzo I, Landa F, Federico A, Gravina AG. Water-assisted colonoscopy in inflammatory bowel diseases: From technical implications to diagnostic and therapeutic potentials. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2024; 16(12): 647-660
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v16/i12/647.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v16.i12.647