Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Mar 16, 2022; 14(3): 129-141
Published online Mar 16, 2022. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v14.i3.129
Published online Mar 16, 2022. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v14.i3.129
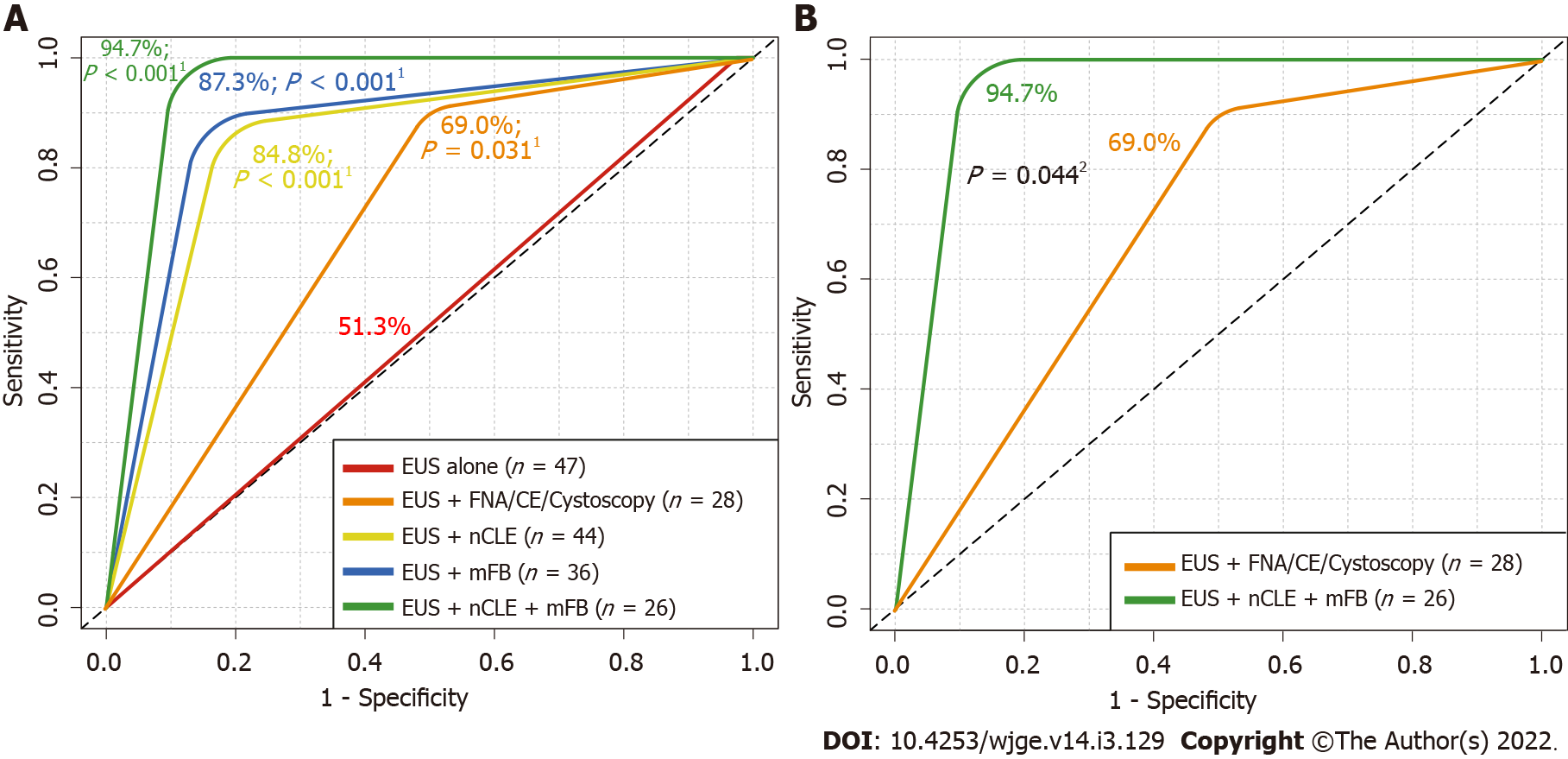
Figure 4 Received operating characteristics describing overall diagnostic accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound alone and in addition with fine needle aspiration or contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasound, needle-based confocal laser-endomicroscopy and/or with direct intracystic micro forceps biopsy for detecting malignancy.
A: Comparison among endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) alone vs additional diagnostic techniques; B: Comparison among EUS alone vs EUS + EUS-guided needle-based confocal laser-endomicroscopy (nCLE) + EUS-guided through-the-needle direct intracystic micro forceps biopsy (mFB). 1DeLong’s test for two received operating characteristics (ROC) curves comparing EUS-alone area under the ROC curve (red line) with EUS + fine needle aspiration (FNA)/contrast-enhanced (CE) (orange line), EUS + nCLE (yellow line), EUS + mFB (blue line) and EUS + nCLE + mFB (green line). 2DeLong’s test for two ROC curves comparing EUS + FNA/CE (orange line) with EUS + nCLE + mFB (green line). EUS: Endoscopic ultrasound; FNA: Fine needle aspiration; Cystoscopy: Fiberoptic probe cystoscopy; nCLE: Endoscopic ultrasound-guided needle-based confocal laser-endomicroscopy; mFB: Endoscopic ultrasound-guided through-the-needle direct intracystic micro forceps biopsy; CE: Contrast-enhanced.
- Citation: Robles-Medranda C, Olmos JI, Puga-Tejada M, Oleas R, Baquerizo-Burgos J, Arevalo-Mora M, Del Valle Zavala R, Nebel JA, Calle Loffredo D, Pitanga-Lukashok H. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided through-the-needle microforceps biopsy and needle-based confocal laser-endomicroscopy increase detection of potentially malignant pancreatic cystic lesions: A single-center study. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2022; 14(3): 129-141
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v14/i3/129.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v14.i3.129