Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Jun 16, 2021; 13(6): 161-169
Published online Jun 16, 2021. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v13.i6.161
Published online Jun 16, 2021. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v13.i6.161
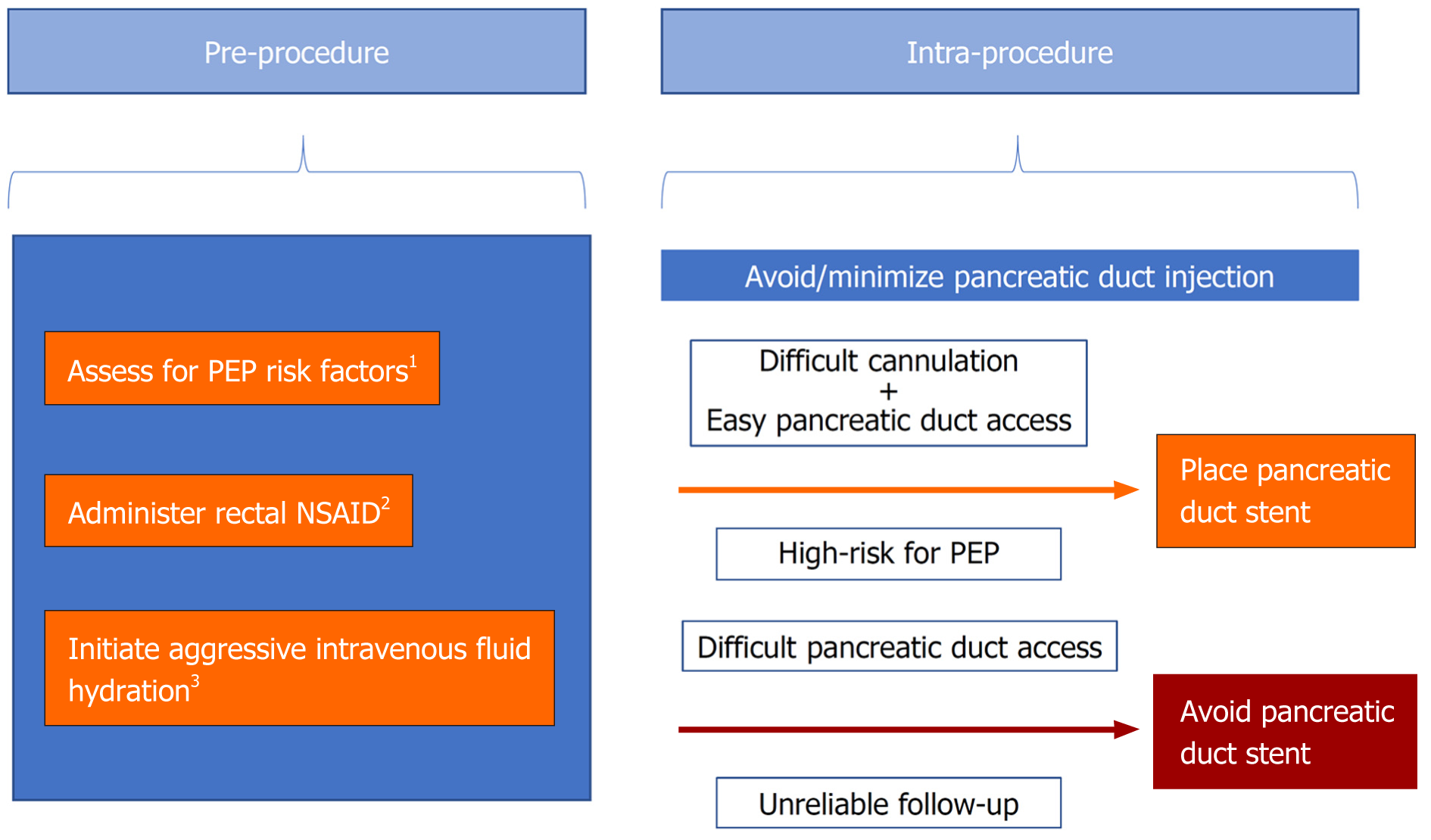
Figure 1 Flow chart illustrating the best-practice approach to post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis prevention and management.
Notably, in patients with complications of underlying advanced liver disease and/or comorbidities such as portal hypertension, coagulopathy, renal dysfunction, and volume overload, the selection of these prophylactic options should be made on a case-by-case basis and, when available, based on clinical evidence. 1Younger age, female sex, normal bilirubin, recurrent pancreatitis, prior post endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis, sphincter of Oddi dysfunction; 2Rectal indomethacin or diclofenac; 3Lactated Ringers preferred, 35-45 mL/kg administered over 8-10 h. PEP: Post endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis; NSAID: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug.
- Citation: Weissman S, Ahmed M, Baniqued MR, Ehrlich D, Tabibian JH. Best practices for prevention of post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2021; 13(6): 161-169
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v13/i6/161.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v13.i6.161