Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Apr 16, 2021; 13(4): 97-110
Published online Apr 16, 2021. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v13.i4.97
Published online Apr 16, 2021. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v13.i4.97
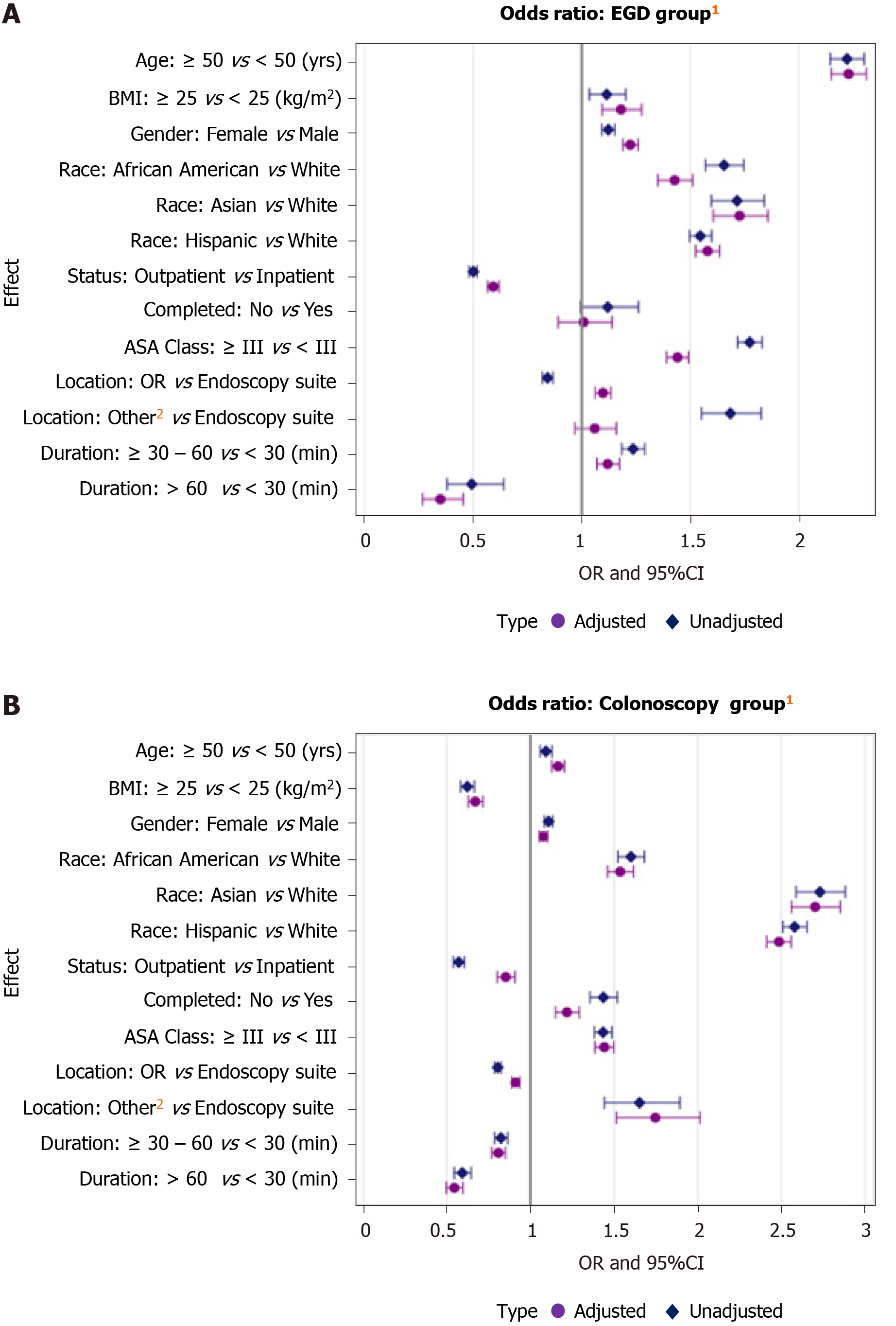
Figure 3 Comparison of esophagogastroduodenoscopy and colonoscopy groups.
A: Esophagogastroduodenoscopy; B: Colonoscopy. Odds ratios based on adjusted and unadjusted analysis comparing “High dose” sedation group and “Low dose” sedation group during esophagogastroduodenoscopy (High dose group = 113281; Low dose group = 25146) and during colonoscopy (High dose group = 194684; Low dose group = 37991). 1Adjusted odds ratios and unadjusted odds ratios for all procedures requiring low dose sedation vs high dose sedation; 2Other site: Ambulatory surgery center, hospital ward, intensive care units, and radiology suite. LD: Low dose; HD: High dose; EGD: Esophagogastroduodenoscopy; OR: Odds ratio; CI: Confidence interval.
- Citation: Passi M, Rahman F, Gurram S, Kumar S, Koh C. Identifying who best tolerates moderate sedation: Results from a national database of gastrointestinal endoscopic outcomes. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2021; 13(4): 97-110
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v13/i4/97.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v13.i4.97