Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Dec 16, 2019; 11(12): 573-588
Published online Dec 16, 2019. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v11.i12.573
Published online Dec 16, 2019. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v11.i12.573
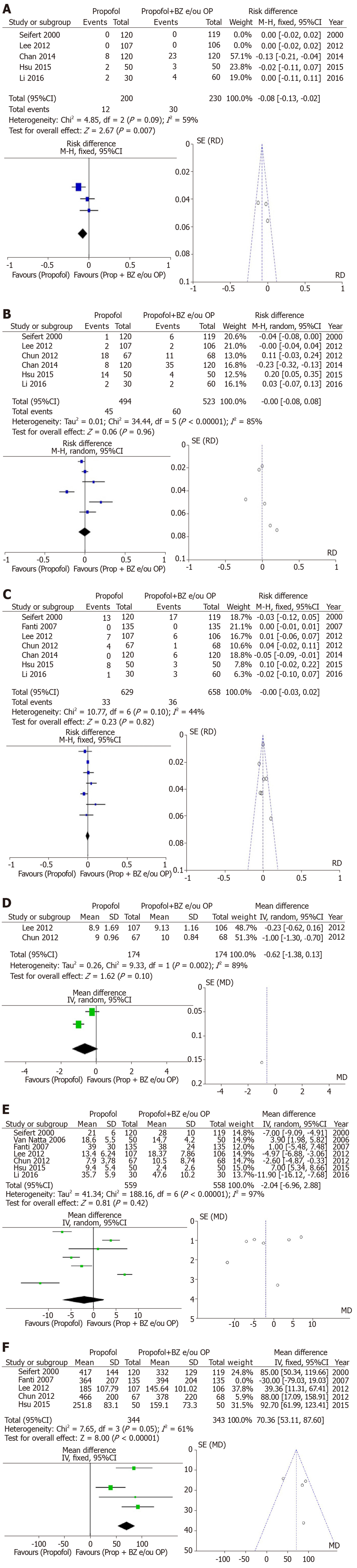
Figure 3 Propofol vs propofol with benzodiazepine and/or opioids - Forest plot of the meta-analysis.
A: Comparing the occurrence of bradycardia between the propofol group and the propofol group associated with benzodiazepine and / or opioid (Prop + BZ and/or OP). Outcome: Bradycardia (defined as HR < 50 bpm); B: Comparing the occurrence of hypotension between the propofol group and (Prop + BZ and/or OP). Outcome: Hypotension (Defined as systolic blood pressure < 90 mmHg); C: Comparing the occurrence of desaturation between the propofol group and Prop + BZ and/or OP. Outcome: Desaturation (Defined as peripheral oxygen saturation of < 90%); D: Comparing patient satisfaction with sedation received for the procedure between propofol group and Prop + BZ and/or OP. Outcome: Patient satisfaction (Visual analog scale - 0 very dissatisfied / 10 very satisfied); E: Comparing patient recovery time after the procedure between the propofol group and Prop + BZ and/or OP. Time to recovery (min); F: Comparing the total dose of propofol administered during procedures between the propofol group and Prop + BZ and/or OP. Outcome: Total dose of propofol given during the procedure (mg).
- Citation: Delgado AAA, de Moura DTH, Ribeiro IB, Bazarbashi AN, dos Santos MEL, Bernardo WM, de Moura EGH. Propofol vs traditional sedatives for sedation in endoscopy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2019; 11(12): 573-588
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v11/i12/573.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v11.i12.573