Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Sep 16, 2018; 10(9): 175-183
Published online Sep 16, 2018. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v10.i9.175
Published online Sep 16, 2018. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v10.i9.175
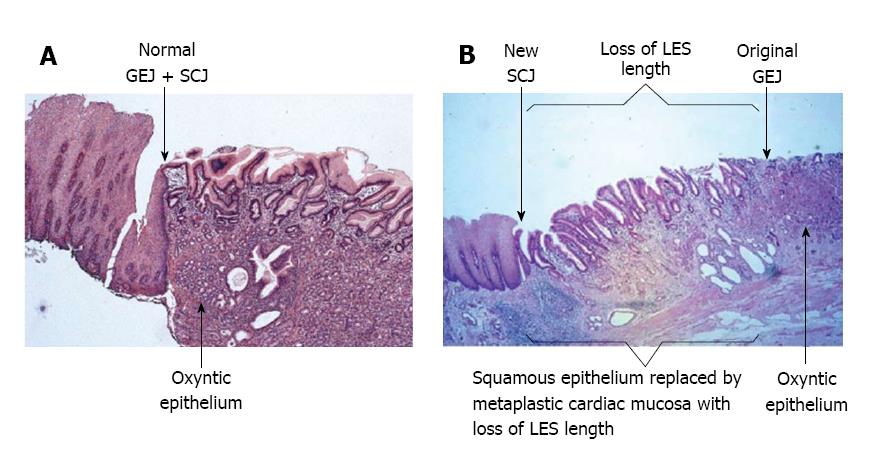
Figure 3 The histology of the squamo-oxyntic gap.
A: The normal junction of the esophagus and stomach is the abutment of the proximal limit of the gastric oxyntic epithelium and the distal limit of the squamous epithelium; B: Squamo-oxyntic gap: Squamous epithelium is replaced by metaplastic cardiac mucosa resulting in loss of LES length, as shown by manometry. Images provided by Dr. Parakrama Chandrasoma. GEJ: Gastroesophageal junction; GERD: Gastroesophageal reflux disease; LES: Lower esophageal sphincter; SCJ: Squamocolumnar junction.
- Citation: Labenz J, Chandrasoma PT, Knapp LJ, DeMeester TR. Proposed approach to the challenging management of progressive gastroesophageal reflux disease. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2018; 10(9): 175-183
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v10/i9/175.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v10.i9.175