Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Sep 16, 2018; 10(9): 175-183
Published online Sep 16, 2018. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v10.i9.175
Published online Sep 16, 2018. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v10.i9.175
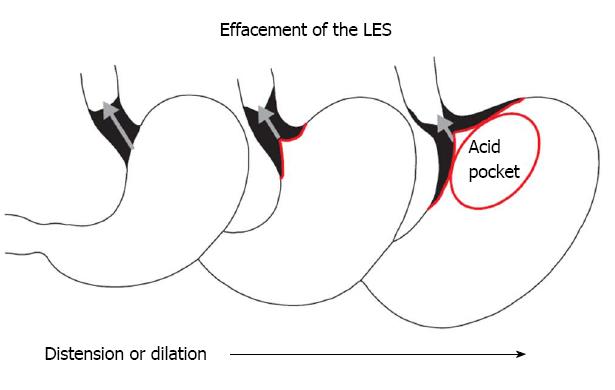
Figure 2 Effacement of the lower esophageal sphincter as a result of gastric distension or dilation.
Exposure of the squamous mucosa covering the effaced portion of the LES to gastric juice results in inflammation, the formation of metaplastic cardiac mucosa, and progressive loss of LES length. The red line represents the squamous epithelial covering of the effaced portion of the LES (in black) as it is taken up by the expanding gastric fundus. LES: Lower esophageal sphincter.
- Citation: Labenz J, Chandrasoma PT, Knapp LJ, DeMeester TR. Proposed approach to the challenging management of progressive gastroesophageal reflux disease. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2018; 10(9): 175-183
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v10/i9/175.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v10.i9.175