Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Nov 16, 2018; 10(11): 340-347
Published online Nov 16, 2018. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v10.i11.340
Published online Nov 16, 2018. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v10.i11.340
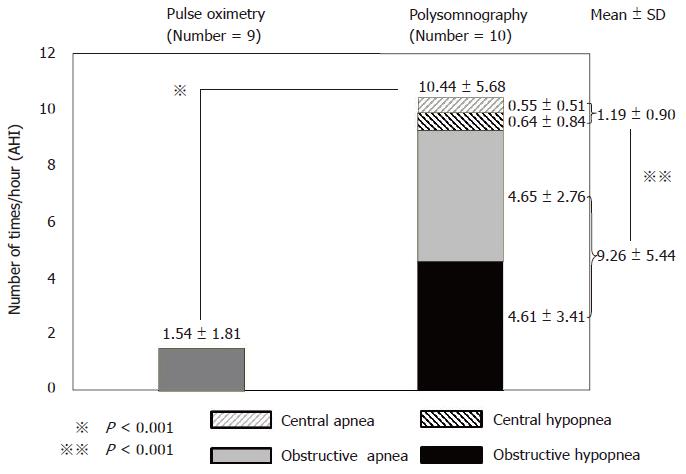
Figure 4 Frequency of respiratory disturbances detected by pulse oximetry and polysomnography.
All patients experienced respiratory disturbances during propofol sedation (total AHI: 10.44 ± 5.68/h). Total apnea hypopnea index (AHI) was significantly greater with polysomnography than with pulse oximetry (1.54 ± 1.81/h, P < 0.001). Obstructive AHI (9.26 ± 5.44/h) was significantly greater than central AHI (1.19 ± 0.90/h, P < 0.001).
- Citation: Urahama R, Uesato M, Aikawa M, Yamaguchi Y, Hayano K, Matsumura T, Arai M, Kunii R, Isono S, Matsubara H. Polysomnographic assessment of respiratory disturbance during deep propofol sedation for endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastric tumors. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2018; 10(11): 340-347
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v10/i11/340.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v10.i11.340