Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Oct 16, 2013; 5(10): 519-522
Published online Oct 16, 2013. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v5.i10.519
Published online Oct 16, 2013. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v5.i10.519
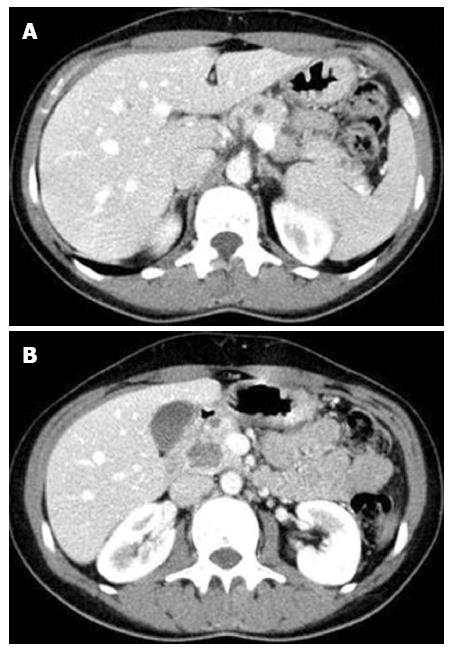
Figure 1 Computed tomography abdominal scan.
A: Small cystic lesions dispersed throughout the pancreas; B: The largest lesion.
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging.
Cyst lesions are bright on T2-weighted images.
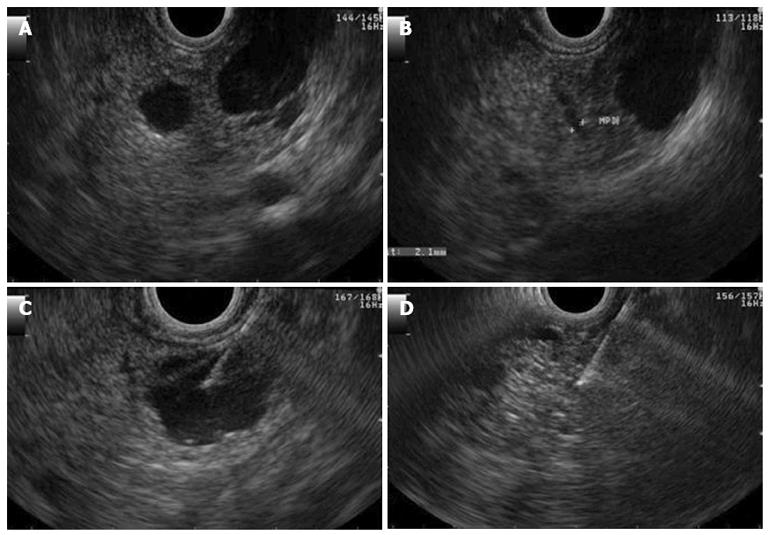
Figure 3 Endosonography.
A, B show a large cyst of 16 mm in diameter without communication or dilatation of the pancreatic duct; C: Demonstrates aspiration of the cyst; D: Demonstrates its appearance after total aspiration.
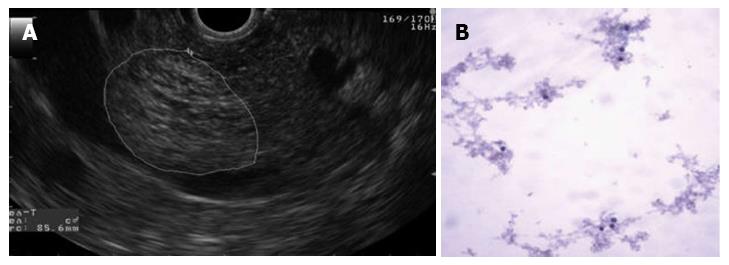
Figure 4 The largest cyst was 23 mm in diameter and was located in the head of the pancreas.
A: Endosonography. Cyst with a honeycomb appearance; B: Cytology (papanicolaou stain, × 100). Benign pancreatic cysts.
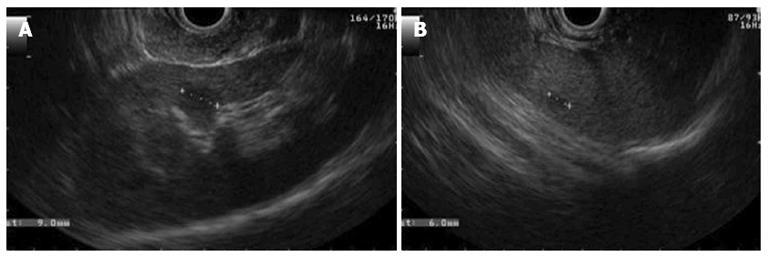
Figure 5 Endosonography.
A: A cyst in the renal cortex; B: A cyst in the spleen.
- Citation: Sousa AL, Sousa D, Figueiredo P, Marques PP, Guerreiro H. Contribution of endosonography in an uncommon case of pancreatic cysts. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2013; 5(10): 519-522
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v5/i10/519.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v5.i10.519