Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Hepatol. Mar 28, 2017; 9(9): 477-486
Published online Mar 28, 2017. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v9.i9.477
Published online Mar 28, 2017. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v9.i9.477
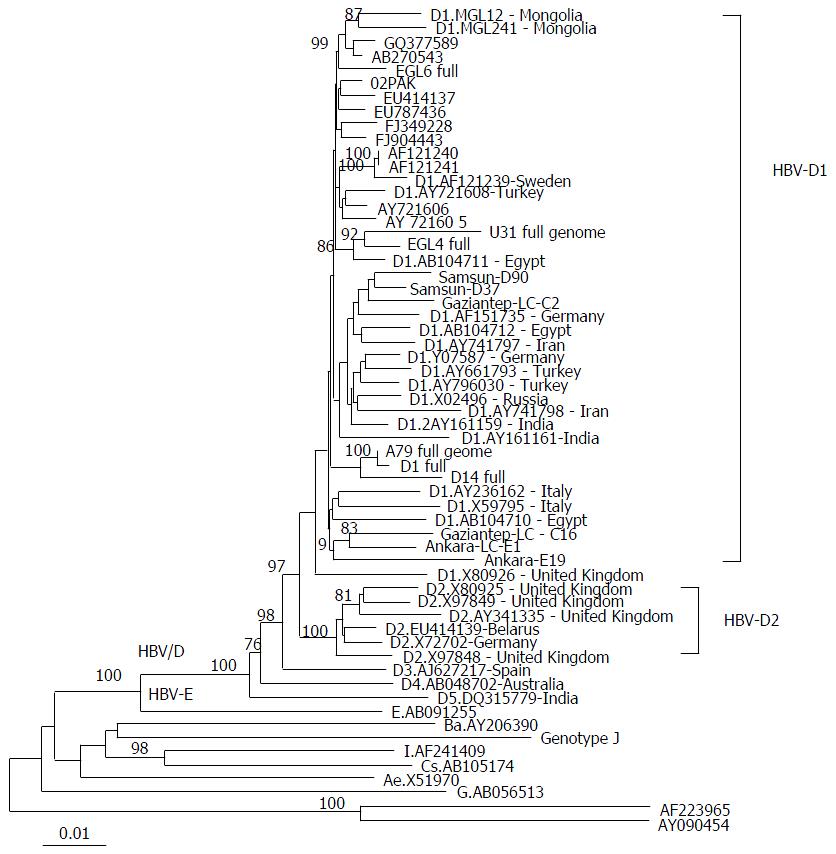
Figure 1 Phylogenetic tree constructed from the nucleotide sequences of the full hepatitis B virus genome.
The phylogenetic tree is constructed by the neighbor joining method and significant bootstrap values (> 75%) are indicated in the tree roots. HBV sequences isolated from the studied cohort are indicated in bold. Reference sequences retrieved from the GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ are indicted by their accession numbers. The country origin of the reference sequences is indicated in brackets. HBV genotypes A-H are indicated in the cluster roots. HBV: Hepatitis B virus.
- Citation: Elkady A, Iijima S, Aboulfotuh S, Mostafa Ali E, Sayed D, Abdel-Aziz NM, Ali AM, Murakami S, Isogawa M, Tanaka Y. Characteristics of escape mutations from occult hepatitis B virus infected patients with hematological malignancies in South Egypt. World J Hepatol 2017; 9(9): 477-486
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v9/i9/477.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v9.i9.477