Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Hepatol. Mar 18, 2017; 9(8): 418-426
Published online Mar 18, 2017. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v9.i8.418
Published online Mar 18, 2017. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v9.i8.418
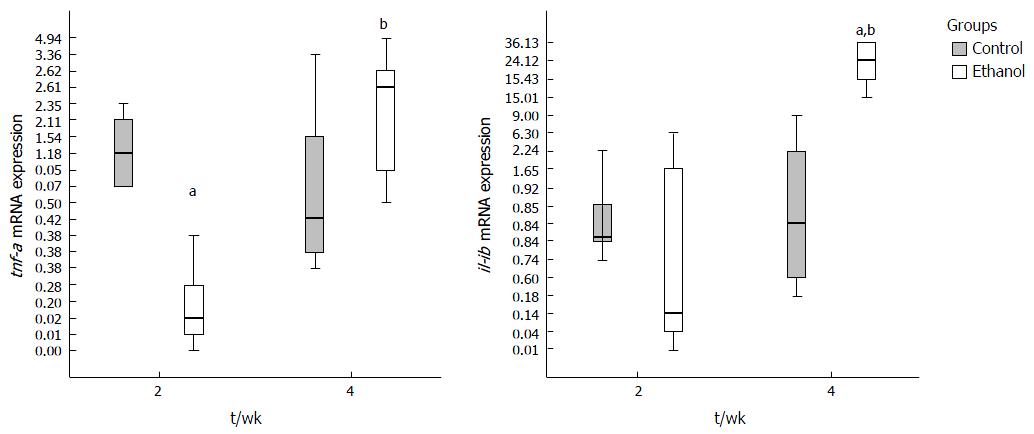
Figure 4 Effect of ethanol on mRNA liver expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1b.
tnf-a was decreased significantly in E group compared to C at 2nd week (P = 0.018) and increased along time up 4th week (P < 0.001), reaching C group levels. Il1-b expression increased between 2 and 4 wk (P = 0.001) and at 4th week there was a significant difference between C and E groups (P = 0.024). Statistical data were determined by the Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn as post hoc test. Values significantly different where indicated: aSignificant statistical difference between 2 and 4 wk; bSignificant statistical difference between C and E groups. P < 0.05 was considered. tnf-a: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; il: Interleukin.
- Citation: Schneider ACR, Gregório C, Uribe-Cruz C, Guizzo R, Malysz T, Faccioni-Heuser MC, Longo L, da Silveira TR. Chronic exposure to ethanol causes steatosis and inflammation in zebrafish liver. World J Hepatol 2017; 9(8): 418-426
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v9/i8/418.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v9.i8.418