Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
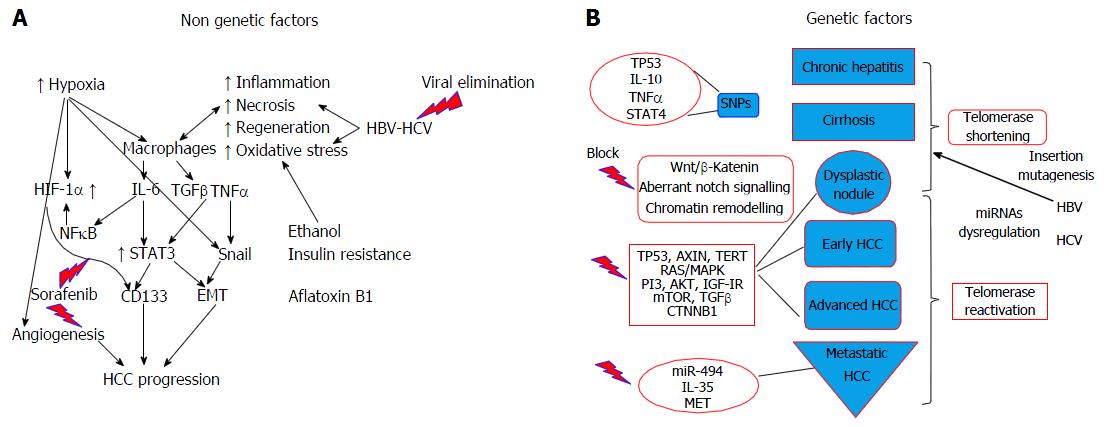
Figure 2 Interplay between genetic and non-genetic factors in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Potential treatment targets. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a complex entity with multifactorial pathogenesis. Control of non-genetic factors (A) (e.g., viral elimination, inhibition of CD133 positive cancer cell overexpression) may lead to alteration of the progress from cirrhosis to HCC. On the other hand, the various genetic irregularities (B) may lead to different HCC profiles with respect to invasiveness (miR-494) or response to treatment. New targeted treatments are also directed against Wnt/β-katenin. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL-6: Interleukin-6; NFκΒ: Nuclear factor-kappa B.
- Citation: Samonakis DN, Kouroumalis EA. Systemic treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma: Still unmet expectations. World J Hepatol 2017; 9(2): 80-90
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v9/i2/80.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v9.i2.80