Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Hepatol. Feb 18, 2016; 8(5): 282-290
Published online Feb 18, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i5.282
Published online Feb 18, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i5.282
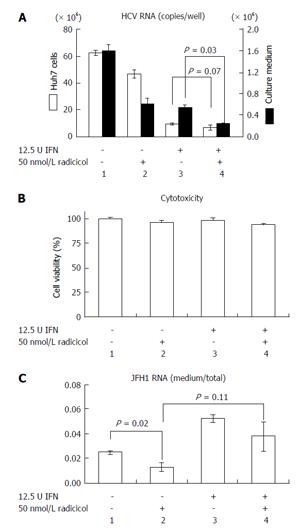
Figure 5 Radicicol and interferon-α have a synergistic effect on hepatitis C virus release into the medium.
A: JFH1/HCVcc-infected Huh-7 cells were treated with 12.5 U INF-α alone, 50 nmol/L radicicol alone, or both for 36 h. The total RNA was prepared from the Huh-7 cells, and the HCV RNA was quantified by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (open columns, the scale on the left of the panel indicates the copies/well). The medium was replaced by fresh medium after 12 h, and the total RNA was prepared from the medium 24 h later. The copy numbers of the HCV RNA in the medium are indicated by the filled columns (scale on the right of the panel); B: The cytotoxic effects of the drugs used in (A) on the Huh-7 cells carrying JFH1/HCVcc; C: The ratios of RNA in the medium to RNA in the total RNA (as described above) are shown. HCV: Hepatitis C virus; HCVcc: Cell culture-derived HCV; INF-α: Interferon-α.
- Citation: Kubota N, Nomoto M, Hwang GW, Watanabe T, Kohara M, Wakita T, Naganuma A, Kuge S. Hepatitis C virus inhibitor synergism suggests multistep interactions between heat-shock protein 90 and hepatitis C virus replication. World J Hepatol 2016; 8(5): 282-290
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v8/i5/282.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i5.282